Suzuki Grand Vitara JB627. Manual — part 171
4A-3 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
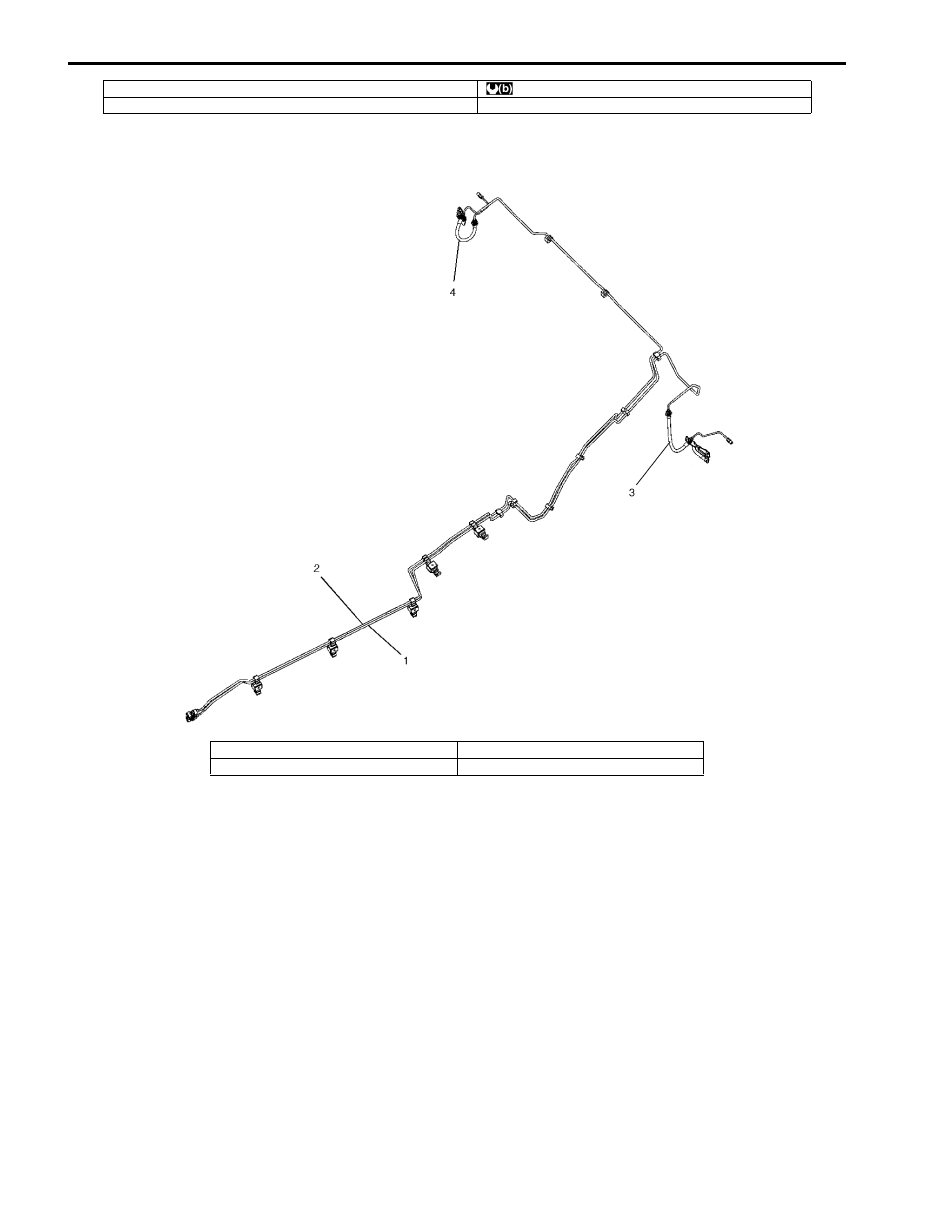
Rear Brake Hose / Pipe Construction
S6JB0B4101003
5. ABS (ESP
®) hydraulic unit / control module assembly
: 11 N
⋅m (1.1 kgf-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
6. Master cylinder
I5JB0A410003-02
1. To left rear brake hose
3. Left rear brake hose
2. To right rear brake hose
4. Right rear brake hose

Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-4
Master Cylinder Assembly Construction
S6JB0B4101004
The master cylinder has two pistons, two pressure seal (3) and two separating seal (4). Its hydraulic pressure is
produced in the primary (A in the figure) and secondary (B) chambers. The hydraulic pressure produced in the primary
chamber (A) acts on the front right and rear left brakes.
Also, the hydraulic pressure produced in the secondary chamber (B) acts on the front left and rear right brakes.
WARNING
!
Brake master cylinder cannot be disassembled. When anything faulty is found in it, it must be replaced
as an assembly.
CAUTION
!
Brake master cylinder cannot be disassembled in principle. Should primary piston (1) have come off
from cylinder while dismounting or handling it, wash it in the same specified fluid as that in reservoir
and place it back in cylinder.
Booster Assembly Construction
S6JB0B4101005
The booster is located between the master cylinder and the brake pedal. It is so designed that the force created when
the brake pedal is depressed is mechanically increased combined with the engine vacuum.
CAUTION
!
• Never disassemble brake booster assembly. If it is found faulty, replace it with new assembly.
• The torque values specified are for dry, unlubricated fasteners. If any hydraulic component is
removed or brake line disconnected, bleed the brake system.
I5JB0A410004-01
2. Secondary piston
6. Secondary piston return spring
8. O-ring
5. Primary piston return spring
7. Grommet
9. Master cylinder body
4A-5 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Brake Diagnosis Note
S6JB0B4104001
Road Test for Brakes
Brakes should be tested on dry, clean, smooth and
reasonably level roadway which is not crowned.
Road test brakes by making brake applications with both
light and heavy pedal forces at various speeds to
determine if the vehicle stops evenly and effectively.
Also drive vehicle to see if it leads to one side or the
other without brake application. If it does, check the tire
pressure, front end alignment and front suspension
attachments for looseness.
See diagnosis flow table for other causes.
Brake Fluid Inspection
Brake fluid leaks
Check the master cylinder fluid levels. While a slight
drop in reservoir level does result from normal lining
wear, an abnormally low level indicates a leak in the
system. In such a case, check the entire brake system
for leakage. If even a slight evidence of leakage is noted,
the cause should be corrected or defective parts should
be replaced.
If fluid level is lower than the minimum level of reservoir,
refilling is necessary.
Fill reservoir with specified brake fluid.
Brake fluid
: Refer to reservoir cap.
CAUTION
!
Since brake system of this vehicle is factory
filled with brake fluid indicated on reservoir
cap, do not use or mix different type of fluid
when refilling; otherwise serious damage will
occur.
Do not use old or used brake fluid, or any
fluid from a unsealed container.
Brakes Symptom Diagnosis
S6JB0B4104002
Condition
Possible cause
Correction / Reference Item
Not enough braking force Brake fluid leakage
Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or pad stained with fluid
Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes
Determine cause and repair.
Poor contact of brake shoe on brake
drum
Repair for proper contact.
Brake shoe stained with fluid or wet with
water
Clean or replace.
Badly worn brake pad and brake shoe
Replace.
Defective wheel cylinders
Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly
Repair or replace.
Air in system
Bleed system.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®), if equipped Check system and replace as necessary.
Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-6
Brake pull
(Brakes not working in
unison)
Pad, disc, shoe and/or drum are wet
with water or stained with fluid in some
brakes
Clean or replace.
Drum-to-shoe clearance out of
adjustment in some brakes.
(malfunctioning auto adjusting
mechanism)
Check for inoperative auto adjusting
mechanism.
Drum is out of round in some brakes
Replace.
Wheel tires are inflated unequally
Inflate equally.
Malfunctioning wheel cylinders
Repair or replace.
Disturbed front end alignment
Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle
Tires with approximately the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses
Check for soft hoses and damaged lines.
Replace with new hoses and new brake piping.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly
Check for stuck or sluggish pistons and proper
lubrication of caliper slide bush.
Loose suspension parts
Caliper should slide. Check all suspension
mountings.
Loose calipers
Check and torque bolts to specifications.
Brake locked
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®)
Check system and replace as necessary.
Excessive pedal travel
(Pedal stroke too large)
Partial brake system failure
Check brake systems and repair as necessary.
Brake fluid leaking
Locate leaking point and repair. Then air bleed.
Air in system (pedal soft / spongy)
Bleed system.
Rear brake system not adjusted
(malfunctioning auto adjusting
mechanism)
Repair auto adjusting mechanism. Adjust rear
brakes.
Bent brake shoes
Replace brake shoes.
Dragging brakes
(Without a very light drag
is present in all disc
brakes immediately after
pedal is released)
Master cylinder pistons not returning
correctly
Replace master cylinder.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses
Check for soft hoses or damaged pipes and
replace with new hoes and/or new brake pipes.
Incorrect parking brake adjustment on
rear brake
Check and adjust to correct specifications.
Weakened or broken return springs in
the rear brake
Replace.
Sluggish parking-brake cables or
linkage
Repair or replace.
Wheel cylinder or brake caliper piston
sticking
Repair as necessary.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®)
Check system and replace as necessary.
Pedal pulsation
(Pedal pulsates when
depressed for braking)
Damaged wheel bearings
Replace wheel hub.
Distorted steering knuckle or rear
suspension knuckle
Replace knuckle.
Excessive disc lateral runout
Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine the disc.
Rear brake drum out of round
Check runout. Repair or replace drum as
necessary.
Brake caliper stick
Check slide pin of brake caliper.
Braking noise
Glazed brake pad and/or brake shoe
Repair or replace brake pad and/or brake
shoe.
Worn or distorted brake pad and/or
brake shoe
Replace brake pad and/or brake shoe.
Worn wheel bearings
Replace wheel hub.
Distorted backing plates
Replace.
Condition
Possible cause
Correction / Reference Item

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст