Suzuki Grand Vitara JB627. Manual — part 92

1D-49 Engine Mechanical:
6) Install valve (1) to valve guide.
Before installing valve to valve guide, apply engine
oil to stem seal, valve guide bore, and valve stem.
7) Install valve spring and spring retainer.
Each valve spring has top end (large-pitch end (1))
and bottom end (small-pitch end (2)). Be sure to
position spring in place with its bottom end (valve
spring retainer side (3)) facing the bottom (valve
spring seat side (4)).
8) Using special tool (Valve lifter), compress valve
spring and fit 2 valve cotters (1) into groove in valve
stem.
Special tool
(A): 09916–14510
(B): 09916–14910
(C): 09916–84511
(D): 09919–28610
Valves and Valve Guides Inspection
S6JB0B1406034
Valve Guides
Using a micrometer and bore gauge, take diameter
readings on valve stems and guides to check stem-to-
guide clearance. Be sure to take reading at more than
one place along the length of each stem and guide.
If clearance exceeds limit, replace valve and valve
guide.
Valve stem-to-guide clearance
IYSQ01141092-01
IYSQ01141093-01
IYSQ01143121-01
Item
Standard
Limit
Valve
stem
diameter
Intake
5.965 – 5.980 mm
(0.2348 – 0.2354 in.)
—
Exhaust
5.940 – 5.955 mm
(0.2339 – 0.2344 in.)
—
Valve
guide
bore
In and
Ex
6.000 – 6.012 mm
(0.2362 – 0.2367 in.)
—
Stem-to-
guide
clearance
Intake
0.020 – 0.047 mm
(0.0008 – 0.0019 in.)
0.07 mm
(0.0028 in.)
Exhaust
0.045 – 0.072 mm
(0.0018 – 0.0028 in.)
0.09 mm
(0.0035 in.)
IYSQ01143122-01
Engine Mechanical: 1D-50
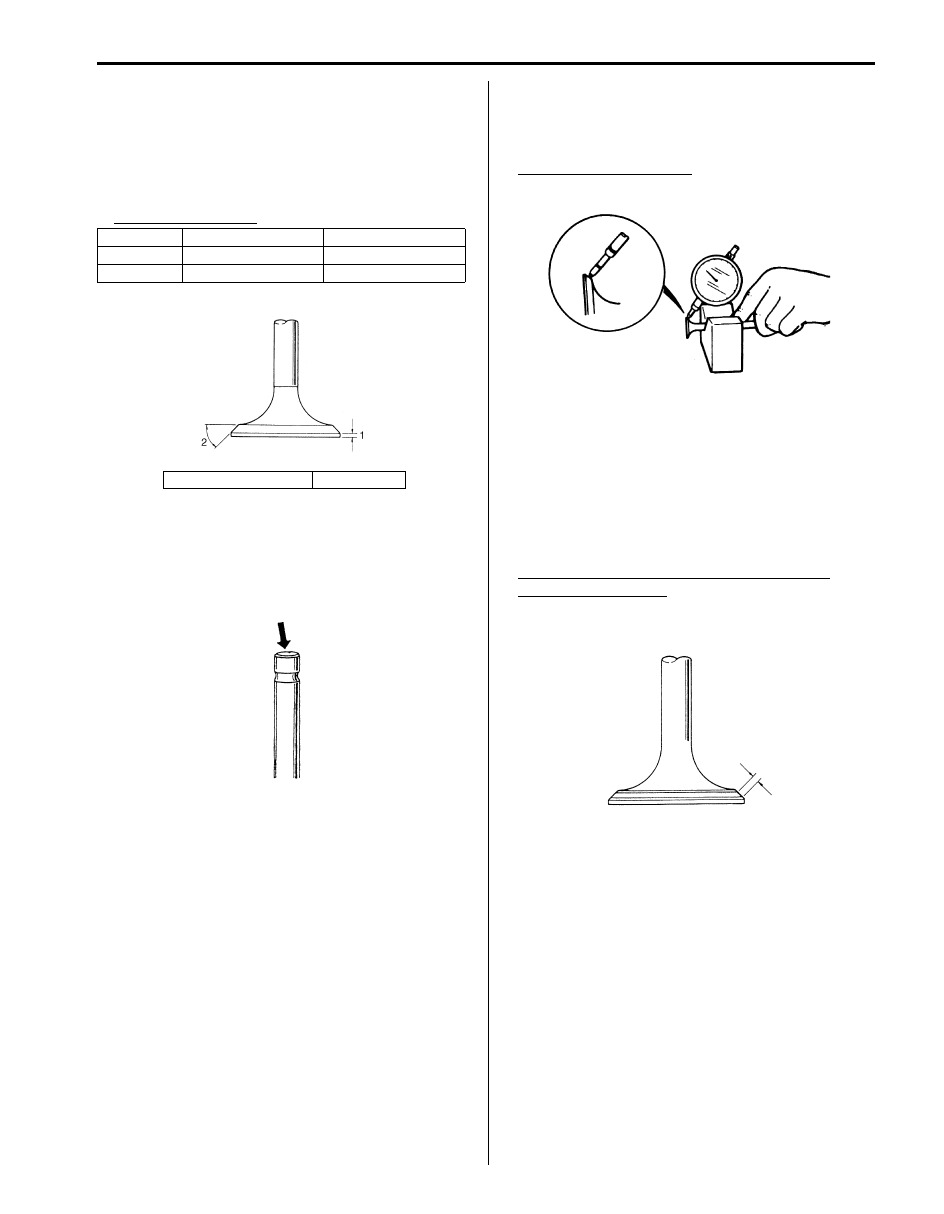
Valves
• Remove all carbon from valves.
• Inspect each valve for wear, burn or distortion at its
face and stem and, as necessary, replace it.
• Measure thickness of valve head. If measured
thickness exceeds limit, replace valve.
Valve specifications
• Inspect valve stem end face for pitting and wear. If
pitting or wear is found, valve stem end may be
resurfaced. But do not grind its taper excessively.
When valve is excessively worn out too much or its
taper is gone, replace it.
• Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge
and “V” block.
To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout exceeds
its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
• Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve
lapping) must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512
in.)
Item
Standard
Limit
Intake
1.0 mm (0.039 in.) 0.6 mm (0.024 in.)
Exhaust
1.2 mm (0.047 in.) 0.7 mm (0.028 in.)
1. Valve head thickness
2. 45
°
IYSQ01141097-01
IYSQ01141098-01
IYSQ01143123-01
IYSQ01141099-01

1D-51 Engine Mechanical:
• Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
a. Exhaust valve seat
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make two cuts as
illustrated in figure. Two cutters must be used: the
1st for making 15
° angle, and the 2nd for making
45
° angle. The 2nd cut must be made to produce
desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
b. Intake valve seat
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in figure. Three cutters must be used:
the 1st for making 15
° angle, the 2nd for making
60
° angle, and the 3rd for making 45° angle. The
3rd cut (45
°) must be made to produce desired
seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
c. Valve lapping
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse
size lapping compound applied to face and the
second with fine-size compound, each time using
valve lapper according to usual lapping method.
Cylinder Head Inspection
S6JB0B1406035
• Remove all carbon from combustion chambers.
NOTE
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to scrape
off carbon. Be careful not to scuff or nick
metal surfaces when decarboning. The same
applies to valves and valve seats, too.
• Check cylinder head for cracks on intake and exhaust
ports, combustion chambers, and head surface.
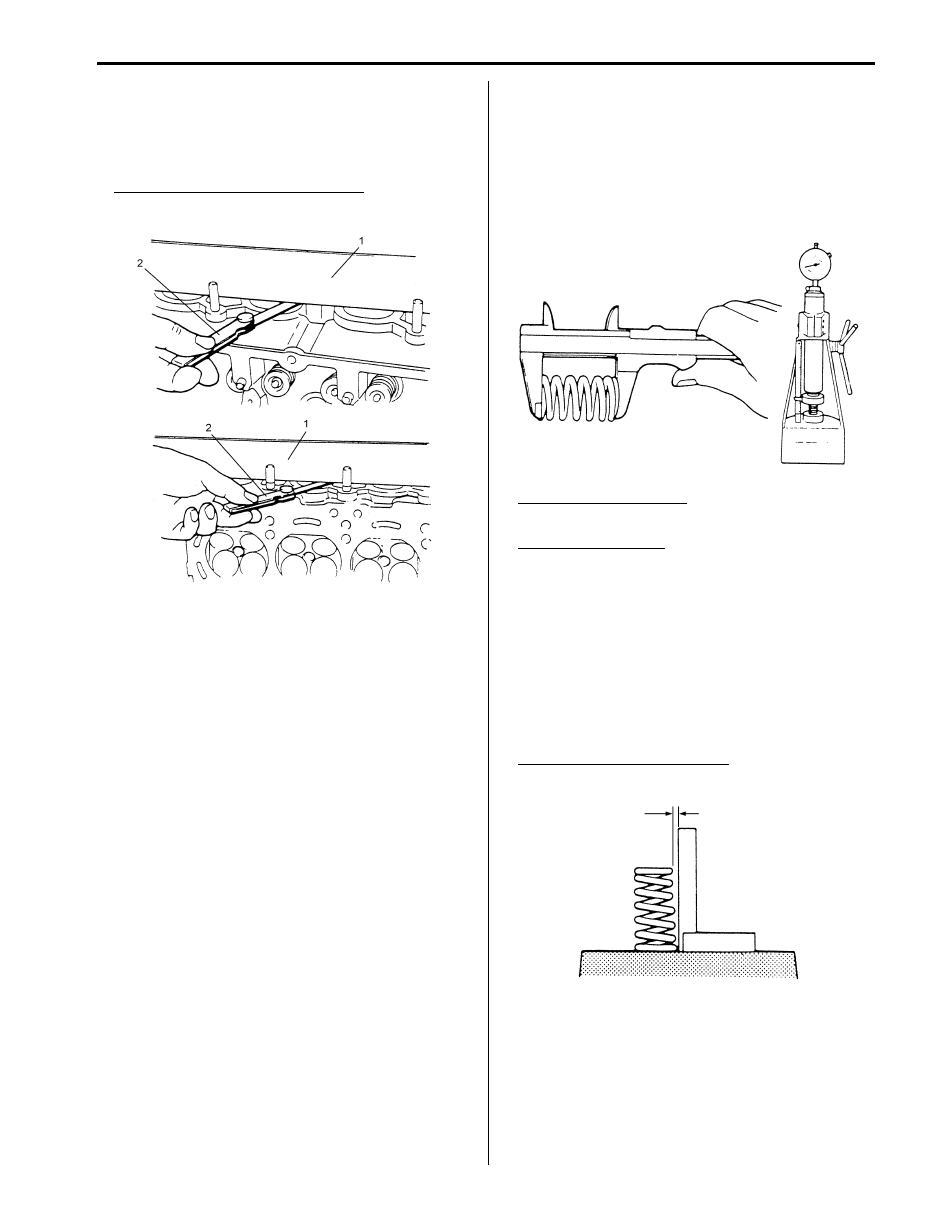
Using straightedge (1) and thickness gauge (2), check
flatness of gasketed surface at a total of 6 locations. If
distortion limit, given below, is exceeded, correct
gasketed surface with a surface plate and abrasive
paper of about #400 (Waterproof silicon carbide
abrasive paper): Place abrasive paper on and over
surface plate, and rub gasketed surface against paper
to grind off high spots. Should this fail to reduce
thickness gauge readings to within limit, replace
cylinder head.
Leakage of combustion gases from this gasketed joint
is often due to warped gasketed surface: such
leakage results in reduced power output.
Cylinder head gasketed surface distortion
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
[A]: Intake valve
[B]: Exhaust valve
IYSQ01141100-01
IYSQ01143124-01
IYSQ01141102-01
I5JA01140016-01
Engine Mechanical: 1D-52
• Distortion of manifold seating faces
Check seating faces of cylinder head for manifolds,
using a straightedge (1) and thickness gauge (2), in
order to determine whether these faces should be
corrected or cylinder head replaced.
Manifold seating surface distortion
Limit: 0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
Valve Springs Inspection
S6JB0B1406036
• Referring to data given below, check to be sure that
each spring is in sound condition, free of any evidence
of breakage or weakening. Remember, weakened
valve springs can cause chatter, not to mention
possibility of reducing power output due to gas
leakage caused by decreased seating pressure.
Valve spring free length
Standard: 51.13 mm (2.0130 in.)
Valve spring preload
Standard: 209 – 241 N (20.9 – 24.1 kg, 46.1 – 53.1
lb) for 37.60 mm (1.480 in.)
Limit: 192 N (19.2 kg, 42.24 lb) for 37.60 mm (1.480
in.)
• Spring squareness
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring
for squareness in terms of clearance between end of
valve spring and square. Valve springs found to
exhibit a larger clearance than limit given below must
be replaced.
Valve spring squareness limit
2.2 mm (0.087 in.)
I5JA01140017-01
IYSQ01141105-01
IYSQ01141106-01

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст