Jaguar XJ (X350). Manual — part 890
5
—
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
6
—
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
7
—
Crankshaft position (CPK) sensor
8
—
Variable camshaft timing oil control solenoid
9
—
Oil temperature sensor
10
—
Oil pressure sensor
11
—
Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor
Item
Part Number
Description
1
—
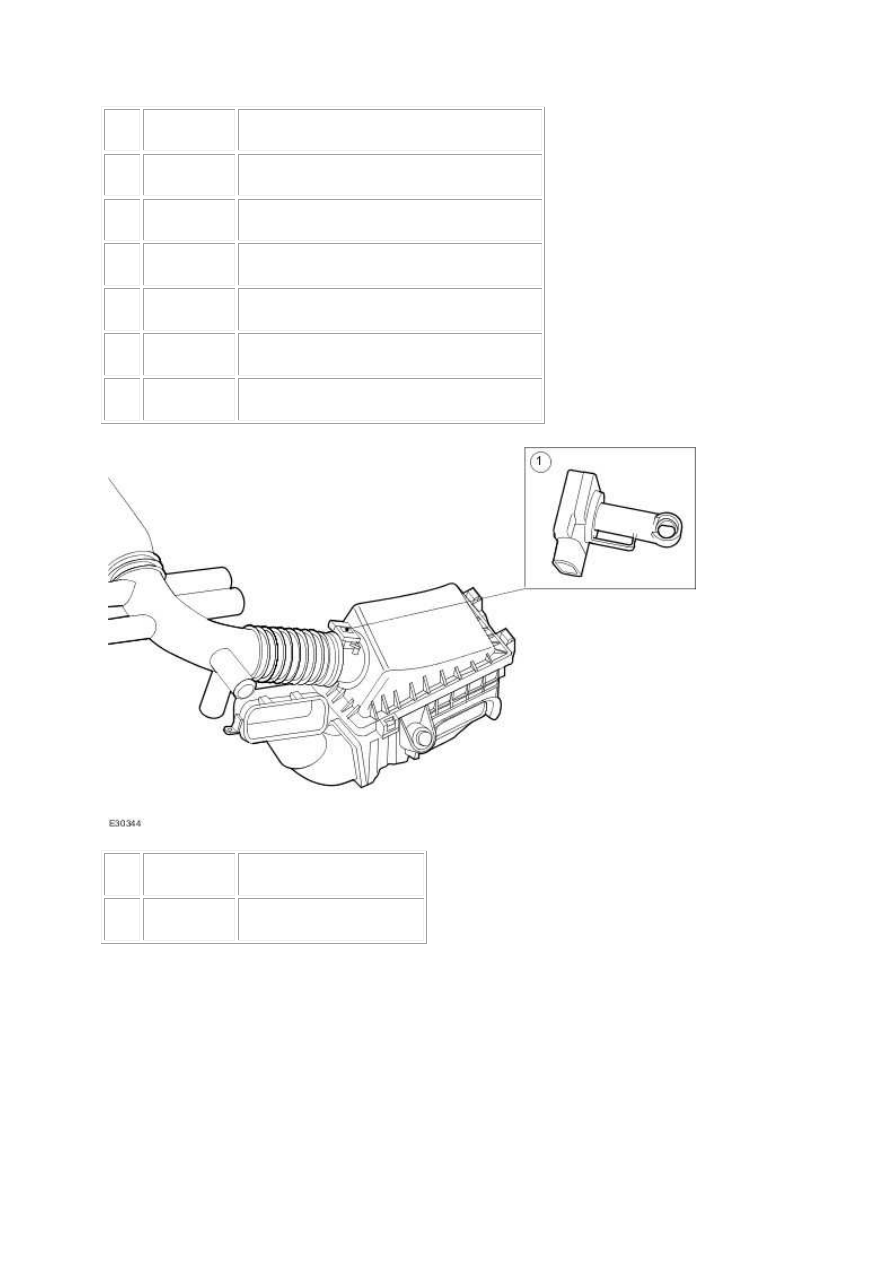
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
Item
Part Number
Description
1
—
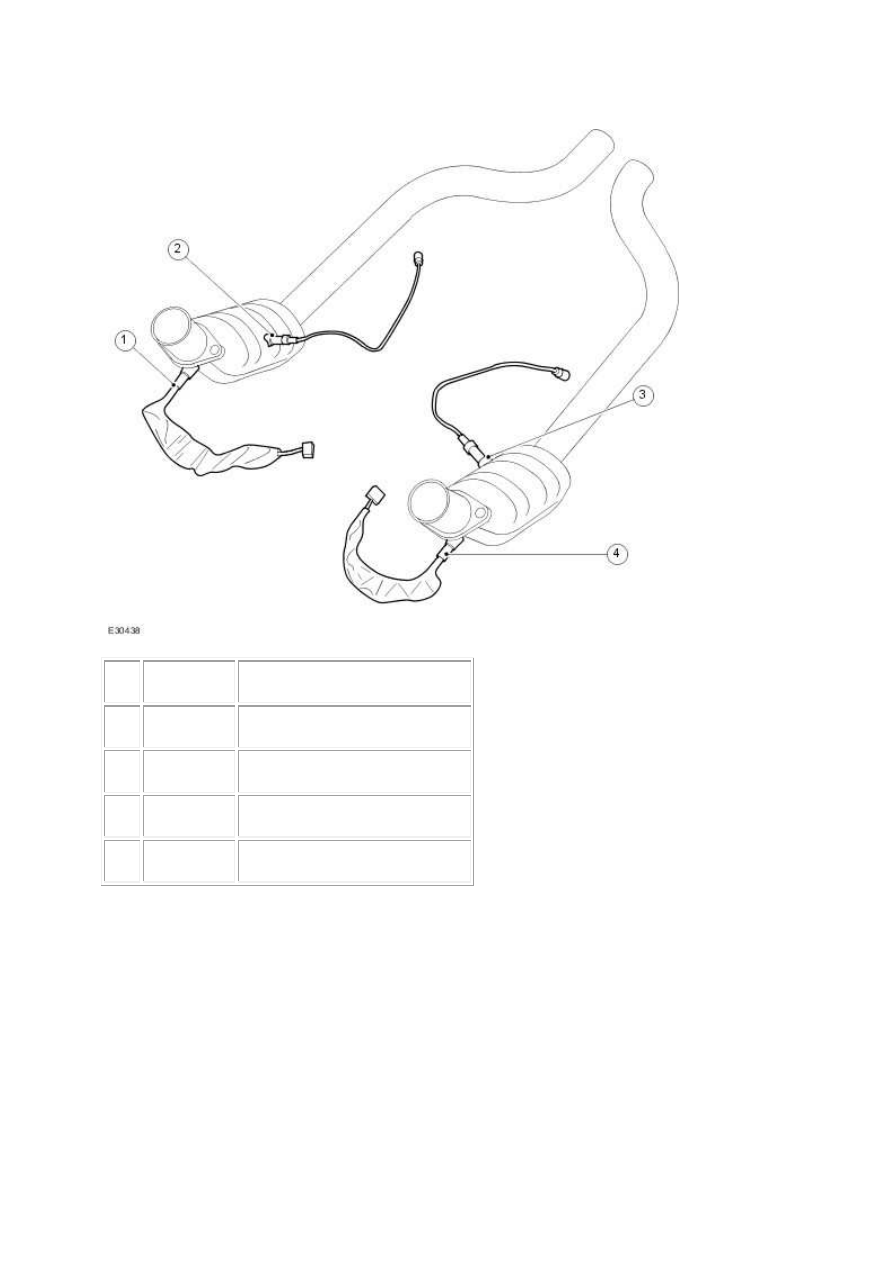
Heated oxygen sensor - RH
2
—
Catalyst monitor sensor - RH
3
—
Catalyst monitor sensor - LH
4
—
Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) - LH
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The electronic engine control system consists of a engine control module (ECM), located behind the
glove compartment, and a number of sensing and actuating devices. The sensors supply the ECM
with input signals which relate to the engine operating conditions and driver requirements. The
sensor information is evaluated by the ECM using the results to activate the appropriate response
from the actuating devices. The system provides the necessary engine control accuracy and
adaptability to:
minimize exhaust emissions and fuel consumption.
www.
provide optimum driver control under all conditions.
minimize evaporative emissions.
provide system diagnostics.
In addition to these functions the ECM also interfaces with other vehicle systems through the
controller area network (CAN).
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
The camshaft position (CMP) sensors monitor the position of both camshafts to allow the ECM to
control the phase of the inlet camshafts relative to the position of the crankshaft.
Variable Camshaft Timing Oil Control Solenoid
The variable camshaft timing oil control solenoid is a hydraulic actuator, which advances and retards
the inlet camshaft timing, thereby altering the camshaft to crankshaft phasing for optimum engine
performance.
Knock Sensors (KS)
The knock sensors (KS) detect combustion knock within the engine cylinders and sends a signal to the
ECM. The ECM uses this information to gradually adjust the ignition timing until the combustion
knock is eliminated.
Mass Air flow (MAF) Sensor
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor informs the ECM of the rate of air flow entering the engine by
producing a voltage which is proportional to the rate of air flow into the engine. The voltage
produced by the MAF sensor increases as the rate of air flow increases. The ECM takes into account
the density of the air entering the air intake system so that it is possible to maintain the required air
to fuel ratio, and to compensate for variations in atmospheric pressure.
Integral to the MAF sensor is the intake air temperature sensor (IAT) which measures the
temperature of the air entering the air intake system. The ECM uses this information to compensate
for higher than normal air intake temperatures.
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
The ECM monitors the angle of the throttle blade within the throttle housing through the throttle
position (TP) sensor. The TP sends a voltage to the ECM which is proportional to the angle of the
throttle plate. The voltage from the TP increases with the angle of the throttle plate. There are two
sensor tracks within the TP sensor.
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is an inductive pulse generator, which scans protrusions on a
pulse ring fitted to the flywheel to inform the ECM of the crankshaft's position and speed. The CKP
sensor produces an alternating voltage. The frequency of this voltage increases proportional to
engine speed.
Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor
The fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor is a pressure transducer device. A vacuum pipe connects to the
intake manifold for manifold pressure. The ECM receives a voltage from the FRP sensor which is
proportional to the fuel pressure in the fuel injection supply manifold.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a thermistor type sensor that provides an input
signal to the ECM which is proportional to the engine coolant temperature. The ECT sensor is a
negative temperature coefficient (NTC) sensor and its resistance decreases with a proportional
increase in engine coolant temperature.
Oil Temperature Sensor
The oil temperature sensor is a thermistor type sensor that provides an input signal to the ECM
which is proportional to the engine oil temperature.
Oil Pressure Switch
The oil pressure switch is connected to the instrument cluster and is not directly part of the
electronic engine control system.
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is a linear characteristic type sensor, fitted forward of the exhaust
system's catalytic converter. The ECM uses this as it's primary sensor to measure the oxygen content
of the exhaust gasses within the exhaust system to provide closed-loop fuelling control.
Catalyst Monitor Sensor
The catalyst monitor sensor is a non-linear characteristic type sensor fitted to the exhaust system's
catalytic converter. The ECM uses this as it's secondary sensor to measure the oxygen content of the
exhaust gasses within the exhaust after they have passed through the catalytic converter. As well as
providing additional closed-loop fuelling control the ECM uses this information to determine the
efficiency of the catalytic converter.
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor. Vehicles with supercharger.
Vehicles with supercharger have an additional intake air temperature sensor located on the right-
hand charge air cooler. The IAT measures the temperature of the air entering the charge air cooler.
The ECM uses this information to compensate for higher than normal air intake temperatures.
www.

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст