SsangYong Actyon Sports II. Manual — part 72
06-5
2110-01
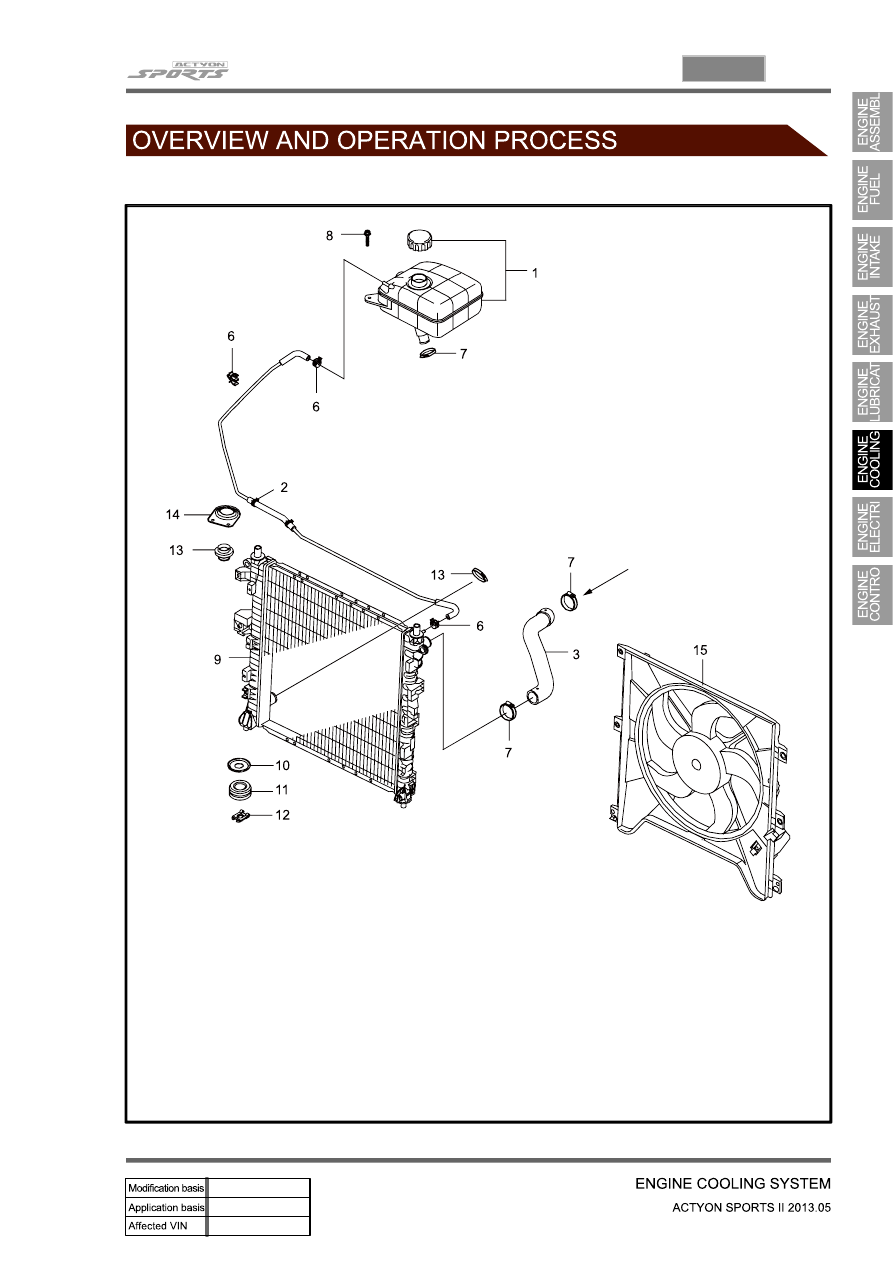
1. COMPONENT LOCATOR
1. Reserver Tank
2. Deaeration Tube
3. Inlet Hose
6. Clamp
7. Clamp
8. Bolt (M6, 2 piece)
9. Radiator
10. Lower Radiator Insulator
11. Plate
12. Clip
13. Upper Radiator Insulator
14. Bracket
15. PWM Electric Fan
06-6
2. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
1) General Description
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions.
When the engine is cold, the cooling system cools the engine slowly or not at all. This slow cooling of
the engine allows the engine to warm up quickly.
The cooling system includes a radiator and recovery subsystem, cooling fans, a thermostat and
housing, a water pump, and a water pump drive belt. The timing belt drives the water pump.
All components must function properly for the cooling system to operation. The water pump draws the
coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through water jackets in the engine block, the
intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the operating
temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the radiator where
it cools.
This system directs some coolant through the hoses to the heat core. This provides for heating and
defrosting.
The coolant reservoir is connected to the radiator to recover the coolant displaced by expansion from
the high temperatures. The coolant reservoir maintains the correct coolant level.
The cooling system for this vehicle has no radiator cap or filler neck. The coolant is added to the cooling
system through the coolant reservoir.
2) Radiator
This vehicle has a lightweight tube-and-fin aluminum radiator. Plastic tanks are mounted on the upper
and the lower sides of the radiator core.
On vehicles equipped with automatic transaxles, the transaxle fluid cooler lines run through the radiator
tank.
A radiator drain plug is on this radiator.
To drain the cooling system, open the drain plug.
3) Coolant Reservoir
The coolant reservoir is a transparent plastic reservoir, similar to the windshield washer reservoir.
The coolant reservoir is connected to the radiator by a hose and to the engine cooling system by another
hose.
As the vehicle is driven, the engine coolant heats and expands. The portion of the engine coolant
displaced by this expansion flows from the radiator and the engine into the coolant reservoir. The air
trapped in the radiator and the engine is degassed into the coolant reservoir.
When the engine stops, the engine coolant cools and contracts. The displaced engine coolant is then
drawn back into the radiator and the engine. This keeps the radiator filled with the coolant to the desired
level at all times and increases the cooling efficiency.
Maintain the coolant level between the MIN and MAX marks on the coolant reservoir when the system is
cold.
06-7
2112-01
4) Water Pump
The belt-driven centrifugal water pump consists of an impeller, a drive shaft, and a belt pulley.
The impeller is supported by a completely sealed bearing.
The water pump is serviced as an assembly and, therefore, cannot be disassembled.
5) Thermostat
A wax pellet-type thermostat controls the flow of the engine coolant through the engine cooling system.
The thermostat is mounted in the thermostat housing to the front of the cylinder head.
The thermostat stops the flow of the engine coolant from the engine to the radiator to provide faster
warm-up, and to regulate the coolant temperature. The thermostat remains closed while the engine
coolant is cold, preventing circulation of the engine coolant through the radiator. At this point, the engine
coolant is allowed to circulate only throughout the heater core to warm it quickly and evenly.
As the engine warms, the thermostat opens. This allows the engine coolant to flow through the radiator
wherethe heat is dissipated. This opening and closing of the thermostat permits enough engine coolant
to enter the radiator to keep the engine within proper engine temperature operating limits.
The wax pellet in the thermostat is hermetically sealed in a metal case. The wax element of the
thermostat expands when it is heated and contracts when it is cooled.
As the vehicle is driven and the engine warms, the engine coolant temperature increases. When the
engine coolant reaches a specified temperature, the wax pellet element in the thermostat expands and
exerts pressure against the metal case, forcing the valve open. This allows the engine coolant to flow
through the engine cooling system and cool the engine.
As the wax pellet cools, the contraction allows a spring to close the valve.
The thermostat begins to open at 87°C(188.6 °F) and is fully open at 102°C(215.6°F). The
thermostat closes at 85°C (187°F).
6) Electric Cooling Fan
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from the engine cooling fans to help prevent personal injury.
This fan is electric and can turn on even when the engine is not running.
-
If a fan blade is bent or damaged in any way, no attempt should be made to repair or reuse the
damaged part. A bent or damaged fan assembly should always be replaced with a new one to
prevent possible injury.
-
06-8
The cooling fans are mounted behind the radiator in the engine compartment. The electric cooling fans
increase the flow of air across the radiator fins and across the condenser on air conditioned (A/C)-
equipped vehicles.
This helps to speed cooling when the vehicle is at idle or moving at low speeds.
All models have two fans. The main fan is 320 mm (12. 6 inches) in diameter with seven blades to aid
the airflow through the radiator and the condenser. An electric motor attached to the radiator support
drives the fan.
The auxiliary fan is 320 mm (12.6 inches) in diameter.
A/C Off or Non-AC Model
▶
The cooling fans are actuated by the engine control module (ECM) using a low-speed cooling
fan relay, a high-speed cooling fan relay and a cooling fan motor relay.
The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed when the coolant temperature reaches
95°C(203°F) and at high speed when the coolant temperature reaches 105°C(221°F).
The ECM will change the cooling fans from high peed to low speed at 100°C(212°F)
and
will turn the cooling fans off at 90°C
(194°F).
-
-
-
A/C On
▶
The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed when the A/C system is on. The ECM will
change to high speed when the high side A/C pressure reaches 1860 kPa (269.8 psi).
The cooling fans will return to low speed when the high side A/C pressure reaches 1378 kPa
(199.8 psi).
-
-
7) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor uses a temperature to control the signal voltage to the
Engine Control Module (ECM).
8) Coolant Temperature Gauge
The coolant temperature gauge controls the instrument panel temperature indicator. The coolant
temperature gauge is located with ECT sensor.

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст