SsangYong Actyon Sports II. Manual — part 54
15-13
0000-00
b. Pilot Injection
Injection before main injection. Consists of 1st and 2nd pilot injection, and Pre-injection
Inject a small amount of fuel before main injection to make the combustion smooth. Also, called as
preliminary injection or ignition injection. This helps to reduce Nox, engine noise and vibration, and to
stabilize the idling.
The injected fuel volume is changed and stopped according to the coolant temperature and intake air
volume.
Pilot injection is much earlier than main injection due to higher engine rpm
Too small injection volume (insufficient injection pressure, insufficient fuel injection volume in main
injection, engine braking)
System failure (fuel system, engine control system)
-
-
-
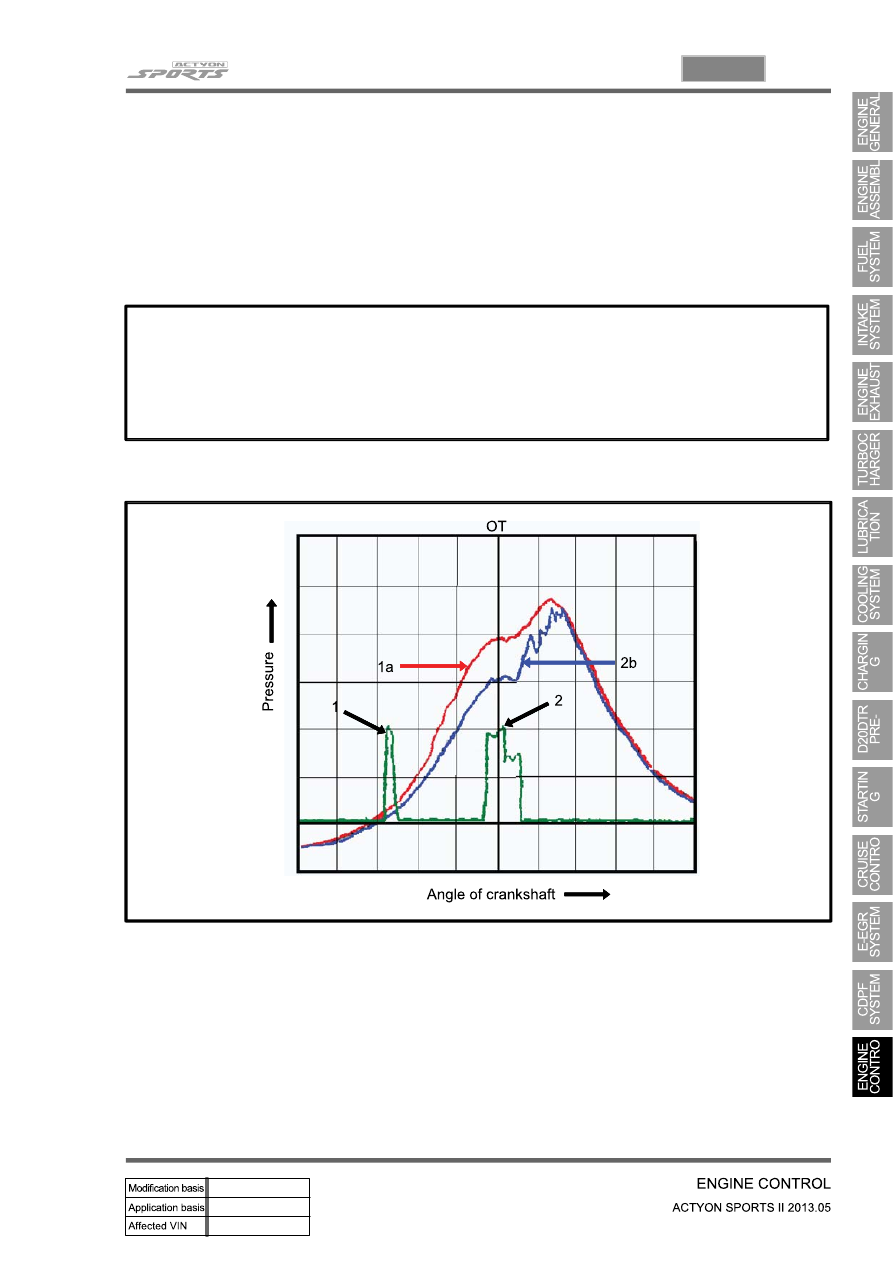
Pilot injection
Main injection
Combustion pressure with pilot injection
Combustion pressure without pilot injection
1.
2.
1a.
2b.
Stop conditions
Combustion pressure characteristic curve for pilot injection
▶
15-14
c. Main Injection
The power of the vehicle is determined by the main fuel injection volume.
Main injection calculates the fuel volume based on pilot injection. The calculation uses the value for
accelerator pedal position, engine rpm, coolant temperature, intake air temperature, boost pressure,
boost temperature and atmospheric pressure etc.
d. Post Injection
Injection after main injection. Consists of After injection, Post 1, Post 2 injection.
Post injection reduces PM and smoke from exhaust gas. No actual output is generated during these
injections, instead, fuel is injected to the unburned gas after main injection to enable fuel activation. The
PM amount in the emission and smoke can be reduced through these processes.
Only up to 5 types of injections can be performed within 1 cycle. If these 7 injections are all performed,
fuel economy and emission performance becomes poor.
15-15
0000-00
(3) Fuel Pressure Control
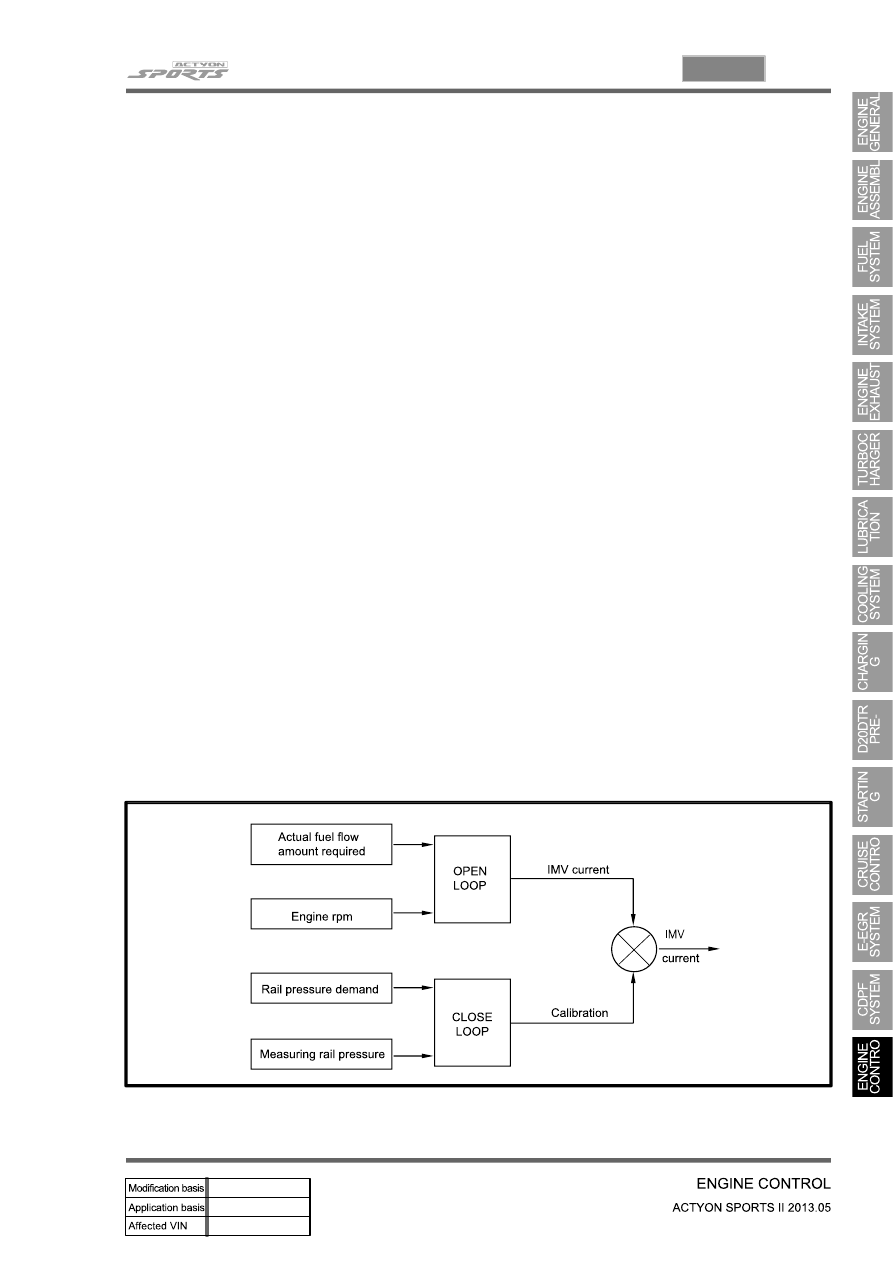
Fuel pressure is controlled by IMV opening according to the calculated value by ECU.
Pressure in the fuel rail is determined according to engine speed and load on the engine.
▶
When engine speed and load are high
The degree of turbulence is very great and the fuel can be injected at very high pressure in order to
optimize combustion.
When engine speed and load are low
The degree of turbulence is low. If injection pressure is too high, the nozzle's penetration will be
excessive and part of the fuel will be sprayed directly onto the sides of the cylinder, causing
incomplete combustion. So there occurs smoke and damages engine durability.
-
-
Fuel pressure is corrected according to air temperature, coolant temperature and atmospheric pressure
and to take account of the added ignition time caused by cold running or by high altitude driving. A
special pressure demand is necessary in order to obtain the additional flow required during starts. This
demand is determined according to injected fuel and coolant temperature.
Open loop determines the current which needs to be sent to the actuator in order to obtain the
flow demanded by the ECU.
▶
Closed loop will correct the current value depending on the difference between the pressure
demand and the pressure measured.
▶
If the pressure is lower than the demand, current is reduced so that the fuel sent to the high pressure
pump is increased.
If the pressure is higher than the demand, current is increased so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is reduced.
-
-
Fuel Pressure
▶
15-16
Pilot injection timing control
▶
The pilot injection timing is determined as a function of the engine speed and of the total flow.
The elements are:
A first correction is made according to the air and coolant temperatures. This correction allows the
pilot injection timing to be adapted to the operating temperature of the engine.
A second correction is made according to the atmospheric pressure. This correction is used to adapt
the pilot injection timing as a function of the atmospheric pressure and therefore the altitude.
-
-
(4) Injection Timing Control
Injection timing is determined by the conditions below.
▶
Coolant temperature
Hot engine - Retarded to reduce Nox
Cold engine - Advanced to optimize the combustion
1.
Atmospheric pressure
Advanced according to the altitude
2.
Warming up
Advanced during warming up in cold engine
3.
Rail pressure
Retarded to prevent knocking when the rail pressure is high
4.
EEGR ratio
Advanced to decrease the cylinder temperature when EGR ratio increases
5.
Main injection timing control
▶
The pulse necessary for the main injection is determined as a function of the engine speed and of the
injected flow.
The elements are:
A first correction is made according to the air and coolant temperatures.
This correction makes it possible to adapt the timing to the operating temperature of the engine.
When the engine is warm, the timing can be retarded to reduce the combustion temperature and
polluting emissions (NOx). When the engine is cold, the timing advance must be sufficient to allow
the combustion to begin correctly.
A second correction is made according to the atmospheric pressure.
This correction is used to adapt the timing advance as a function of the atmospheric pressure and
therefore the altitude.
A third correction is made according to the coolant temperature and the time which has passed since
starting.
This correction allows the injection timing advance to be increased while the engine is warming up
(initial 30 seconds). The purpose of this correction is to reduce the misfiring and instabilities which are
liable to occur after a cold start.
-
-
-

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст