Isuzu KB P190. Manual — part 751
Engine Mechanical – V6
Page 6A1–227
Page 6A1–227
2
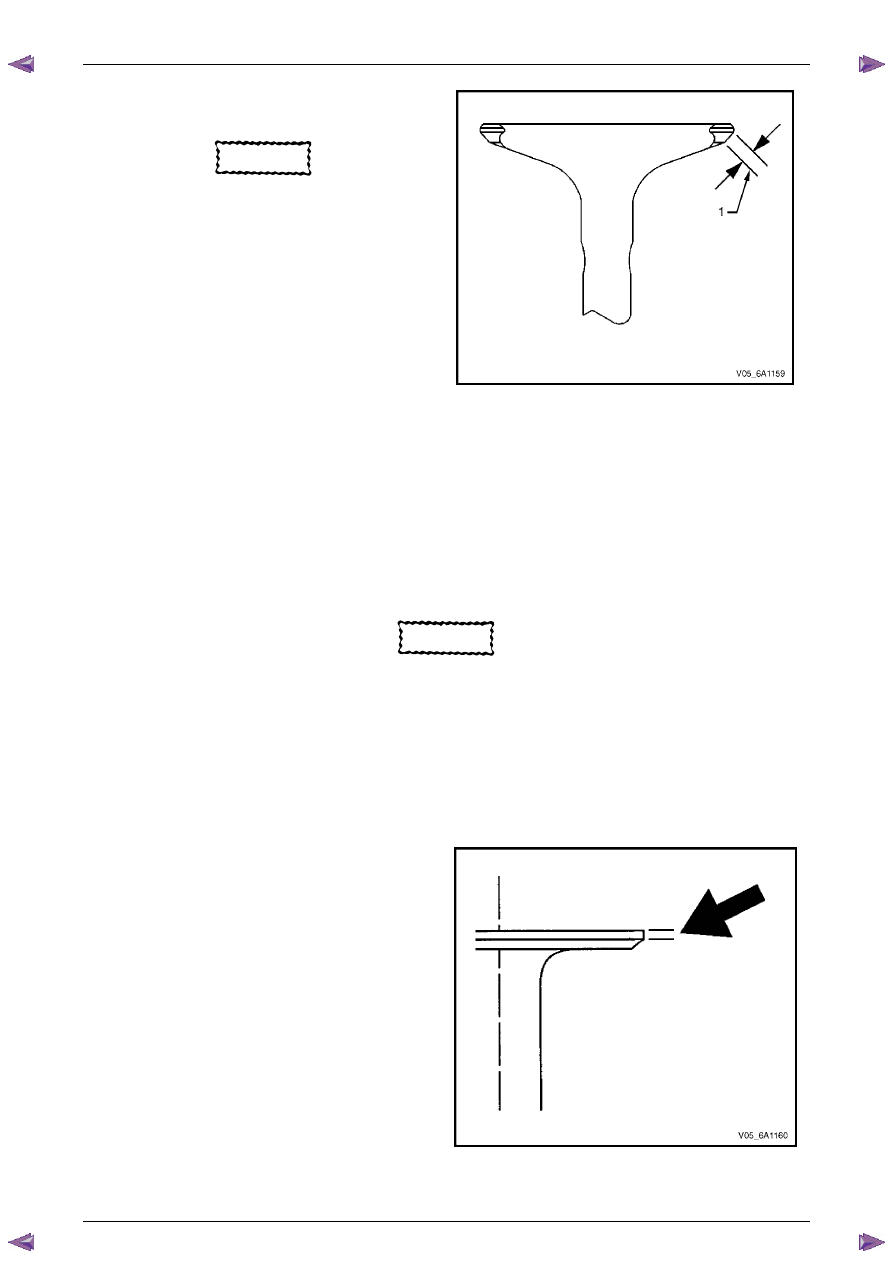
Measure the seat width on the valve face (1) using a
correct scale.
CAUTION
The seat contact area must be at least
0.5 mm from the outer diameter (margin) of
the valve. If the contact area is too close to
the margins, the seat must be reconditioned
to move the contact area away from the
margin.
3
Compare the measurements with the specifications,
refer to
5 Specifications
.
4
If the seat widths are acceptable, check the valve
seat roundness, refer to Valve Seat Roundness
Measurement Procedure in this Section.
5
If the seat width is not acceptable, grind the valve
seat to bring the width back to specification. Correct
valve seat width is critical to providing the correct
amount of valve heat dissipation, refer to Valve and
Seat Reconditioning Procedure in this Section.
Figure 6A1 – 383
Valve Seat Roundness Measurement Procedure
1
Measure the valve seat roundness using a dial indicator attached to a tapered pilot installed in the guide. The pilot
should have a slight bind when installed in the guide.
CAUTION
The correct size pilot must be used. Do not
use adjustable diameter pilots. Adjustable
pilots may damage the valve guides.
2
Compare your measurements with the specifications, refer to
5 Specifications
.
3
If the valve seat exceeds the roundness specification, grind the valve and valve seat, refer to Valve and Seat
Reconditioning Procedure in this Section.
4
If new valves are being used, the valve seat roundness must be within 0.05 mm.
Valve Margin Measurement Procedure
1
Measure the valve margin using an appropriate scale.
2 Refer
to
5 Specifications
for minimum valve margin
and compare them to your measurements.
3
If the valve margins are beyond specification, replace
the valves.
4
If the valve margins are within specification and do
not require refacing, test the valve for seat
concentricity, refer to Valve-to-Seat Concentricity
Measurement Procedure in this Section.
Figure 6A1 – 384
Engine Mechanical – V6
Page 6A1–228
Page 6A1–228
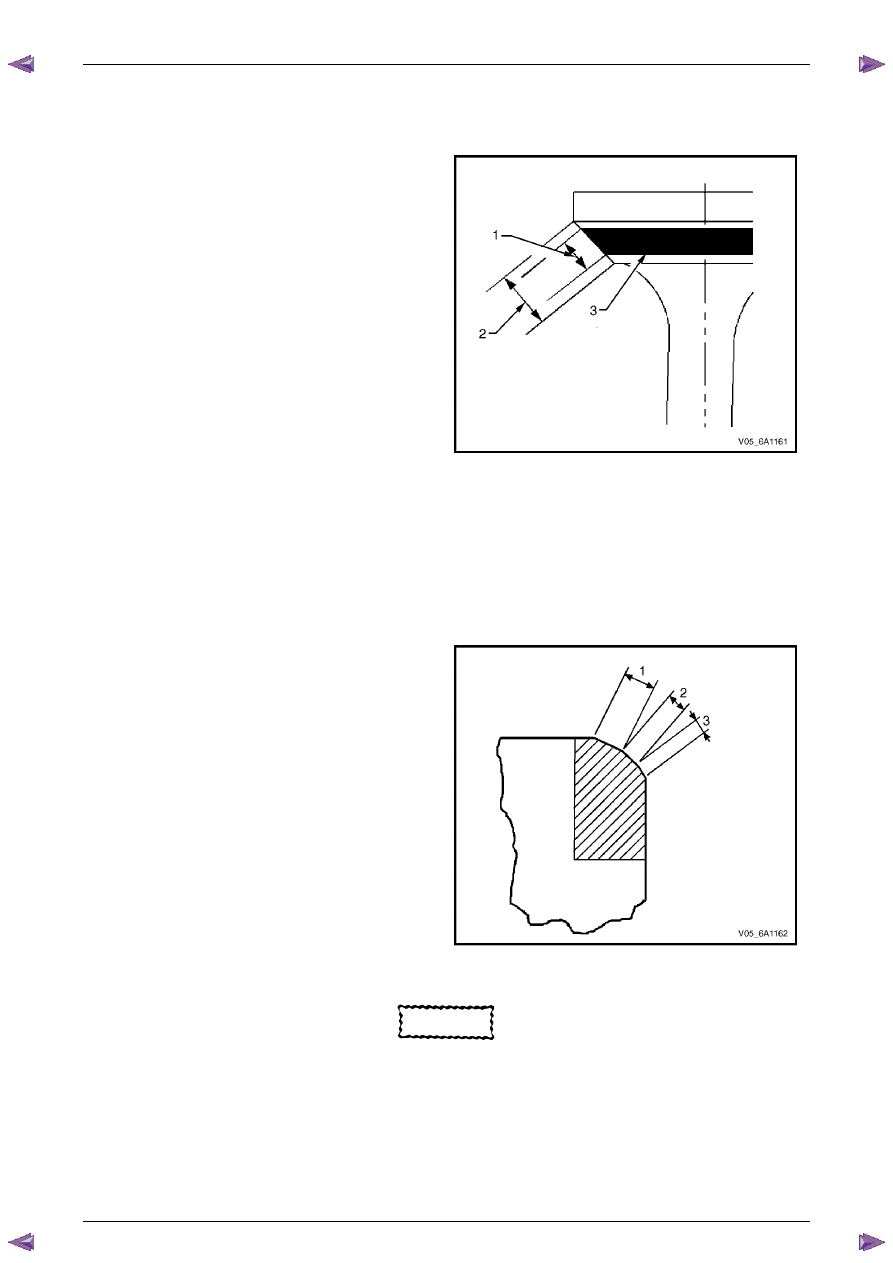
Valve-to-Seat Concentricity Measurement Procedure
Checking the valve-to-seat concentricity determines whether the valve and seat are sealing correctly.
Measure the valve face and the valve seat to ensure correct valve sealing.
1
Coat the valve face lightly with blue dye (3).
2
Install the valve in the cylinder head.
3
Turn the valve against the seat with enough pressure
to wear off the dye.
4
Remove the valve from the cylinder head.
5
Inspect the valve face.
N O T E
•
If the valve face is concentric, providing a
correct seal, with the valve stem, a continuous
mark (1) will be made around the entire face (2).
•
The wear mark must be at least 0.5 mm from
the margin of the valve. If the wear mark is too
close to the margin, the seat must be
reconditioned to move the contact area away
from the margin.
•
If the face is not concentric with the stem, the
mark will not be continuous around the valve
face. The valve should be refaced or replaced
and the seat must be reconditioned, refer to
Valve and Seat Reconditioning Procedure in
this Section.
Figure 6A1 – 385
Valve and Seat Reconditioning Procedure
If the valve seat width, roundness or concentricity are beyond specifications, grind the seats in order to ensure correct
heat dissipation and prevent the build up of carbon on the seats.
If valve seat reconditioning is required, reface the valve face, unless a new valve is used.
1
Grind the valve seats (2) to the correct angle
specification, refer to
5 Specifications
.
2
Using the correct angle specification, grind and
relieve the valve seats (1) to correctly position the
valve seating surface (2) to the valve.
3
Using the correct angle specification, grind and
undercut the valve seats (3) to narrow the valve seat
widths to the specifications, refer to
5 Specifications
.
4
If the original valve is being used, grind the valve to
the specifications, refer to
5 Specifications
. Measure
the valve margin again after grinding, refer to Valve
Margin Measurement Procedure in this Section.
Replace the valve if the margin is out of specification.
New valves do not require grinding.
5
When grinding the valves and seats, grind off as little
material as possible. Cutting valve seat results in
lowering the valve spring pressure.
6
Install the valve in the cylinder head.
Figure 6A1 – 386
CAUTION
If using refaced valves, lap the valves into the
seats with a fine grinding compound. The
refacing and reseating operations should
leave the refinished surfaces smooth and true
so that minimal lapping is required. Excessive
lapping will groove the valve face and prevent
a good seat when hot.
Engine Mechanical – V6
Page 6A1–229
Page 6A1–229
N O T E
• Clean any remaining lapping compound from
the valve and seat with solvent and
compressed air prior to final assembly.
• If fitting new valves, do not lap the valves
under any condition.
7
After obtaining the correct valve seat width in the cylinder head, measure the valve stem height, refer to Valve
Stem Height Measurement Procedure in this Section.
8
If the valve stem height is acceptable, test the seats for concentricity, refer to Valve-to-Seat Concentricity
Measurement Procedure in this Section.
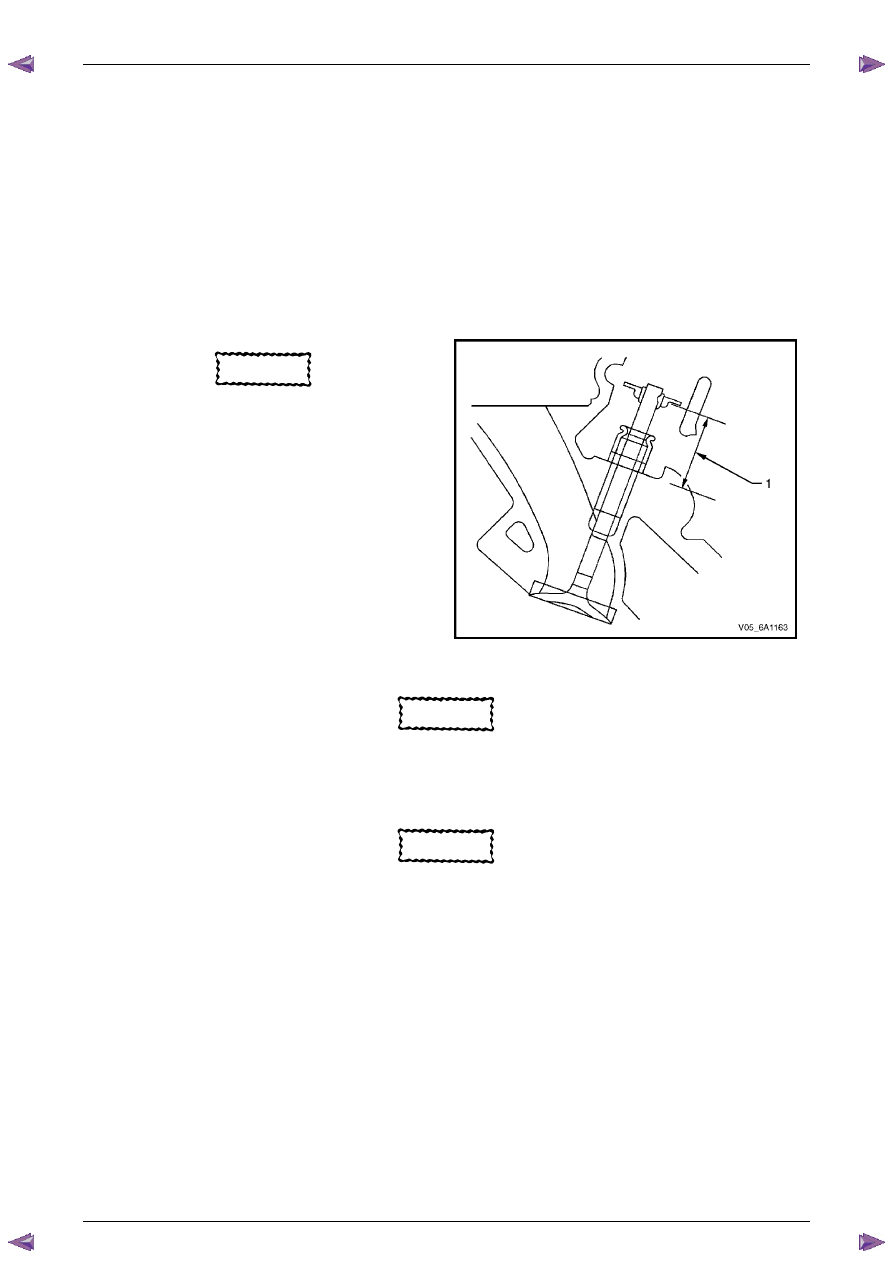
Valve Stem Height Measurement Procedure
CAUTION
To determine the valve stem height
measurement, measure from the valve
spring seat to the valve spring retainer.
1
Install the valve into the valve guide.
2
Ensure the valve is seated to the valve seat.
3
Install the valve stem oil seal.
4
Install the valve spring retainer and valve stem keys.
5
Measure the distance (1) between the cylinder head
to the bottom of the valve spring retainer, refer to
5 Specifications
.
6
If the maximum height specification is exceeded, a
new valve should be installed and the valve stem
height re-measured.
Figure 6A1 – 387
CAUTION
Do not grind the valve stem tip. The tip of the
valve is hardened and grinding the tip will
eliminate the hardened surface causing
premature wear and possible engine damage.
CAUTION
Do not use shims to adjust valve stem height.
The use of shims will cause the valve spring
to bottom out before the camshaft lobe is at
peak lift and engine damage could result.
7
If the valve stem height still exceeds the maximum height specification, the cylinder head must be replaced.

Engine Mechanical – V6
Page 6A1–230
Page 6A1–230
Assemble
1
Install the cylinder head coolant threaded plugs (1)
and tighten to the correct torque specification.
Cylinder head threaded plug . . . . . . . ..31.0 Nm
Figure 6A1 – 388
2
Install the cylinder head oil gallery expansion
plugs (1).
Figure 6A1 – 389
CAUTION
• Never reuse a valve stem oil seal. Always
use new seals when assembling the
cylinder head.
• Force should only be applied to the valve
spring contact area of the new valve stem
oil seal during installation.
3
Fit the valve stem oil seals onto the guides using Tool
No. EN-46116 (1).
4
Push and twist the valve stem oil seal into position on
the valve guide until the seal positively locks on the
guide using Tool No. EN-46116.
5
Lubricate the valve stem and valve guide ID with
clean engine oil.
Figure 6A1 – 390

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст