DAF LF45, LF55 Series. Manual — part 202
©
200505
1-1
Safety instructions
CE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
ΛΦ45/55 series
2
6
1. SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1.1 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Fuel
Diesel fuel is an extremely
flammable liquid, and must not be
exposed to naked flames or come
into contact with hot surfaces. The
diesel fuel fumes remaining in an
empty fuel tank form an extremely
explosive mixture.
When fuel system components are being
removed, some fuel will escape.
To keep this spillage to a minimum, unscrew the
tank cap to release any overpressure.
Any spilled fuel must be collected, bearing in
mind the risk of fire.
Exhaust gases
Do not run the engine in an enclosed or
unventilated area.
Make sure exhaust fumes are properly extracted.
Exhaust gases contain carbon
monoxide.
Carbon monoxide is a deadly
colourless and odourless gas,
which, when inhaled, deprives the
body of oxygen, leading to
asphyxiation. Serious carbon
monoxide poisoning may result in
brain damage or death.
Moving parts
Remain at a safe distance from rotating and/or
moving components.
Various fluids
Various oils and lubricants used on the vehicle
may constitute a health hazard.
This also applies to engine coolant, windscreen
washer fluid, refrigerant in air-conditioning
systems, battery acid and clutch fluid.
So avoid inhaling and direct contact.
Electrical short-circuit
Always disconnect the battery's earth connection
during repair or maintenance operations for
which the electric power supply is not required.
}
}
CE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
1-2
©
200505
Safety instructions
6
ΛΦ45/55 series
2
©
200505
2-1
General
CE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
ΛΦ45/55 series
2
6
2. GENERAL
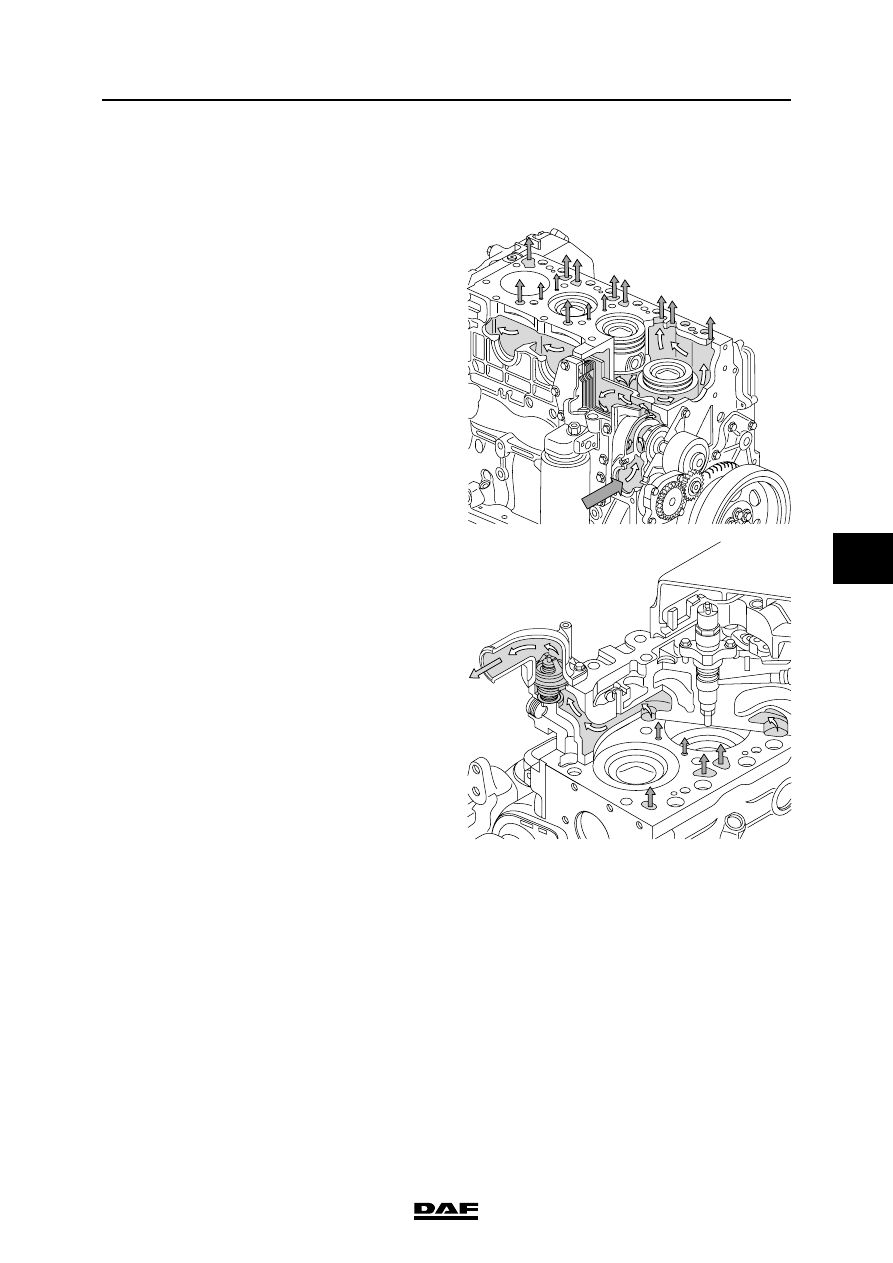
2.1 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION, COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system consists of a water pump, a
radiator, a header tank, an oil cooler, an air
compressor, a thermostat housing with one
thermostat and pipes.
The water pump is located below the thermostat
in the engine block.
The thermostat housing is part of the cylinder
head.
From the delivery side of the water pump, the
coolant is directed to the oil cooler via an opening
at the back of the water pump. Afterwards the
coolant flows to the cylinder block.
The coolant flows through the cylinder block,
along the cylinder liners, and up to the cylinder
head.
The coolant leaves the cylinder head through the
thermostat housing.
Depending on the coolant temperature, the
thermostat distributes the coolant flow to the
radiator or back to the water pump.
The coolant transported to the radiator enters the
radiator at the top and leaves it at the bottom.
From the bottom of the radiator, the coolant is
returned to the water pump via the return pipe.
The connection pipe to the header tank is also
connected to the return pipe from the radiator.
When the coolant heats up, it flows to the header
tank. When the coolant cools down, it will flow
back from the header tank.
The oil cooler is not only intended to cool the
lubricating oil, but also to heat it in a "cold"
engine.
From the cylinder block, some of the coolant
flows through the air compressor.
From the air compressor, the coolant is returned
to the engine block via a pipe.
The pipe which takes the coolant to the cab
heater is connected to the cylinder head. From
the heater, the coolant is returned to the water
pump via a pipe.
M201133
M201134
CE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
2-2
©
200505
General
6
ΛΦ45/55 series
2

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст