Isuzu KB P190. Manual — part 817
Engine Management – V6 – General Information
Page 6C1-1–26
The EOP sensor provides a voltage signal to the ECM that
is a function of engine oil pressure. It does this through a
series of deformation resistors (1), which change resistance
when a mechanical force is applied. This force is applied to
the resistors by a diaphragm on which the engine oil
pressure acts (2).
The sensor has an internal evaluation circuit (3) and is
provided with a 5 V reference voltage, a ground and a signal
circuit.
Figure 6C1-1 – 28
4.12 Fuel
Injectors
A fuel injector is a solenoid device that is controlled by the
ECM. The six injectors deliver a precise amount of fuel into
each of the intake ports as required by the engine.
Figure 6C1-1 – 29
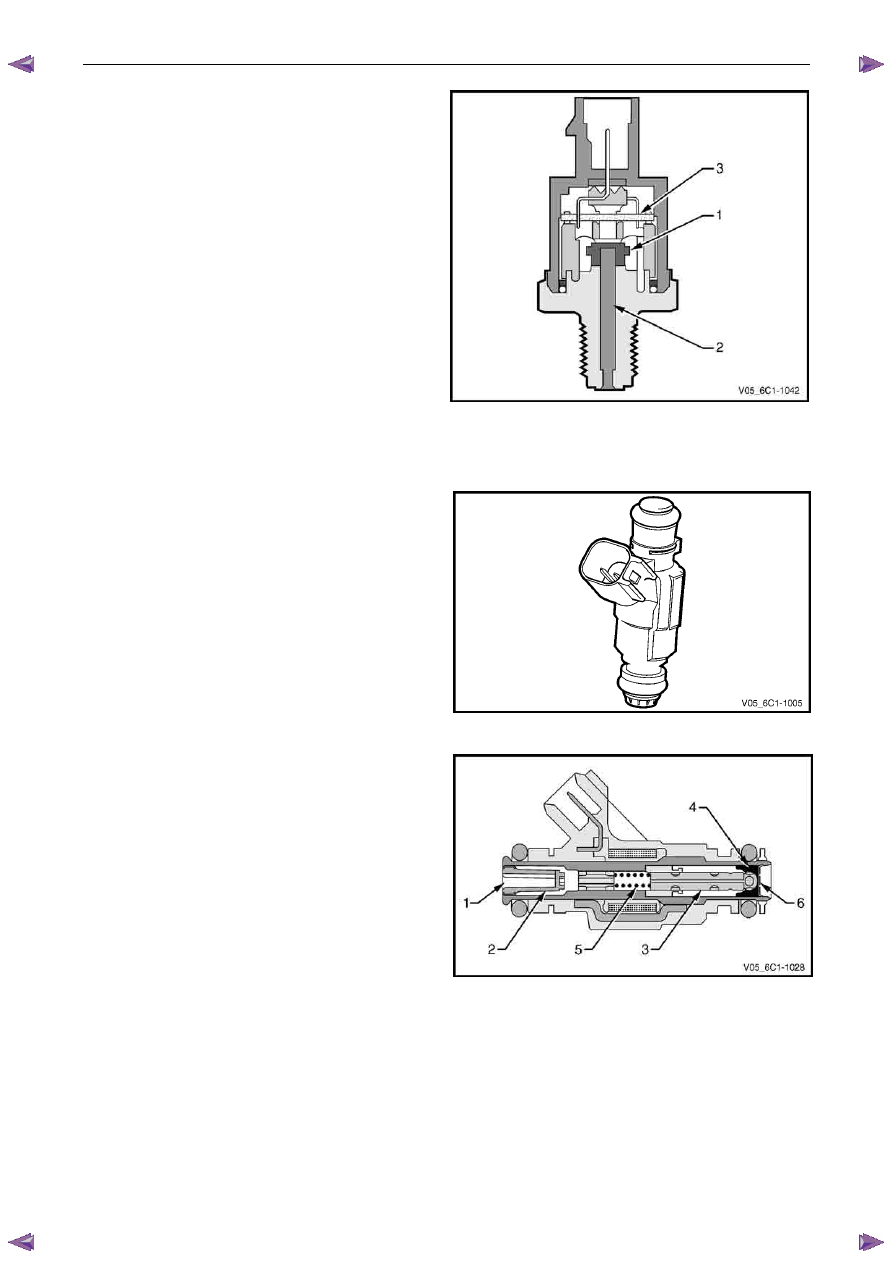
The fuel port (1) connects to the fuel rail. A strainer (2) is
provided in the port to protect the injector from fuel
contamination.
In the de-energised state (no voltage), the valve needle and
sealing ball assembly (3) are held against a cone-shaped
valve seat (4) by spring force (5) and fuel pressure.
When the injector is energised by the ECM, the valve
needle, which has an integral armature, is moved upward by
the injector solenoids magnetic field, un-seating the ball.
An orifice plate (6), located at the base of the injector has
openings that are arranged in such a way that two fuel
sprays emerge from the injector.
Each fuel spray is then directed at one of the intake valves,
causing the fuel to become further vaporised before entering
the combustion chamber.
Figure 6C1-1 – 30
Engine Management – V6 – General Information
Page 6C1-1–27
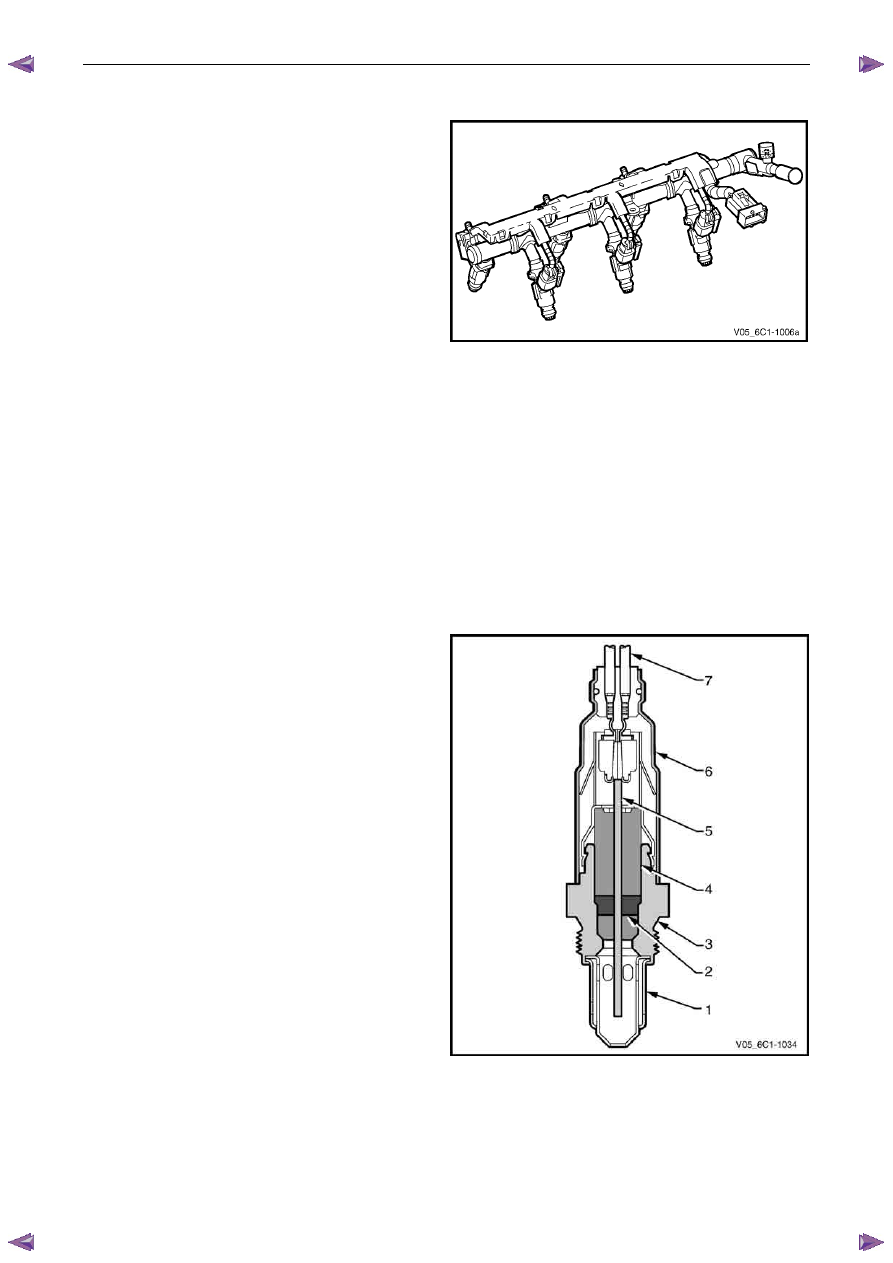
4.13 Fuel Rail Assembly
The fuel rail assembly is mounted on the lower intake
manifold and distributes the fuel to each cylinder through
individual fuel injectors. The fuel rail assembly consists of:
•
the pipe that carries fuel to each injector,
•
a fuel pressure test port,
•
six individual fuel injectors,
•
wiring harness, and
•
wiring harness tray.
Figure 6C1-1 – 31
4.14 Heated Oxygen Sensors
The heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) are mounted in the exhaust system and enable the ECM to measure oxygen
content in the exhaust stream. The ECM uses this information to accurately control the air / fuel ratio, because the
oxygen content in the exhaust gas is indicative of the air / fuel ratio of engine combustion.
When the sensor is cold, it produces little or no signal voltage, therefore the ECM only reads the HO2S signal when the
HO2S sensor is warm. As soon as the HO2S are warm and outputting a usable signal, the ECM begins making fuel
mixture adjustments based on the HO2S signals. This is known as closed loop mode.
The HFV6 engine has four HO2S, one LSU 4.2 wide-band planar type HO2S upstream of the catalytic converter in each
exhaust pipe, and one LSF 4.2 two-step planar type HO2S in each exhaust pipe downstream of the catalytic converter.
LSF 4.2 Two-step Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors
The LSF 4.2 two-step planar heated oxygen sensors have
four wires:
•
The internal heater element supply, which has 12 V
continually applied whenever the ignition is on.
•
Heater element ground – The ECM applies pulse
width modulated (PWM) ground to the HO2S heater
control circuit to control the rate at which the sensor
heats up. This reduces the risk of the sensor being
damaged from heating up too quickly under certain
conditions such as extreme cold temperatures. Once
the sensor has reached the desired operating
temperature, the ECM will monitor and continue to
maintain the sensor temperature.
•
Sensor signal to the ECM.
•
Sensor ground.
Legend
1 Protective
Tube
2
Ceramic Seal Packing
3 Sensor
Housing
4
Ceramic Support Tube
5
Planar Measuring Element
6 Protective
Sleeve
7 Connection
Cable
Figure 6C1-1 – 32
Engine Management – V6 – General Information
Page 6C1-1–28
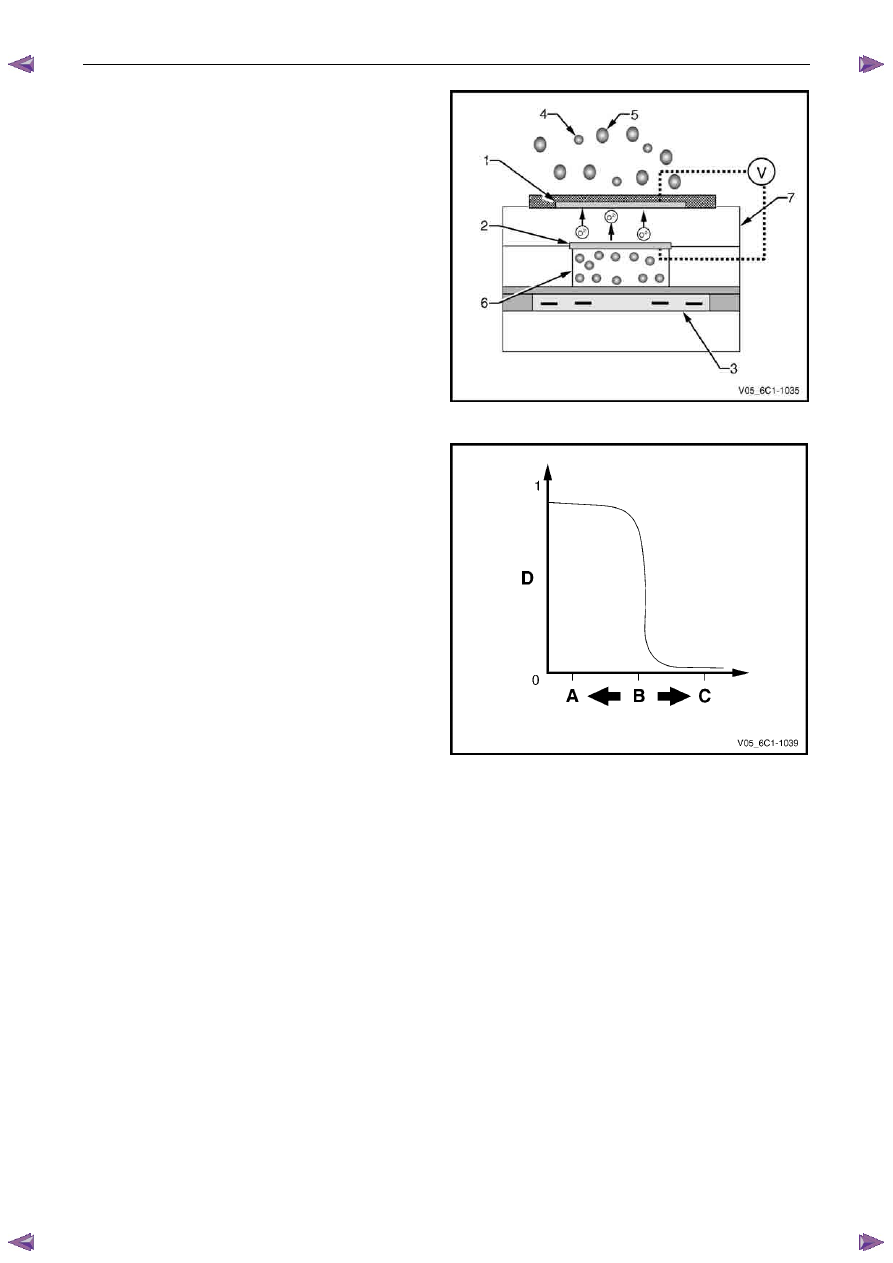
Measurement is achieved by comparing the oxygen content
of the exhaust gas to the oxygen content of a reference gas
(outside air) using the Nernst principle. Oxygen molecules
from the exhaust gas will accumulate on the outer electrode,
while oxygen molecules from the reference gas will
accumulate on the inner electrode. This creates a voltage
difference across the Nernst cell, between the two
electrodes, which is the signal voltage to the ECM.
Legend
1 Outer
Electrode
2 Inner
Electrode
3 Heater
Element
4
Oxygen Molecule (in exhaust stream)
5
Other Molecules (in exhaust stream)
6
Reference Gas (outside air)
7 Nernst
Cell
V Signal
Voltage
Figure 6C1-1 – 33
When the fuel system is correctly operating in the closed-
loop mode, the oxygen sensor voltage output is rapidly
changing several times per second, fluctuating from
approximately 100mV (high oxygen content – lean mixture)
to 900mV (low oxygen content – rich mixture). The transition
from rich to lean occurs quickly at about 450-500 mV (air
flow (A/F) ratio 14.7:1, or lambda = 1). Due to this, two-step
HO2S sensors are also known as switching type HO2S
sensors.
Legend
A Rich
Mixture
B
A/F Ratio 14.7:1 (Lambda = 1)
C Lean
Mixture
D Sensor
Voltage
Figure 6C1-1 – 34
Engine Management – V6 – General Information
Page 6C1-1–29
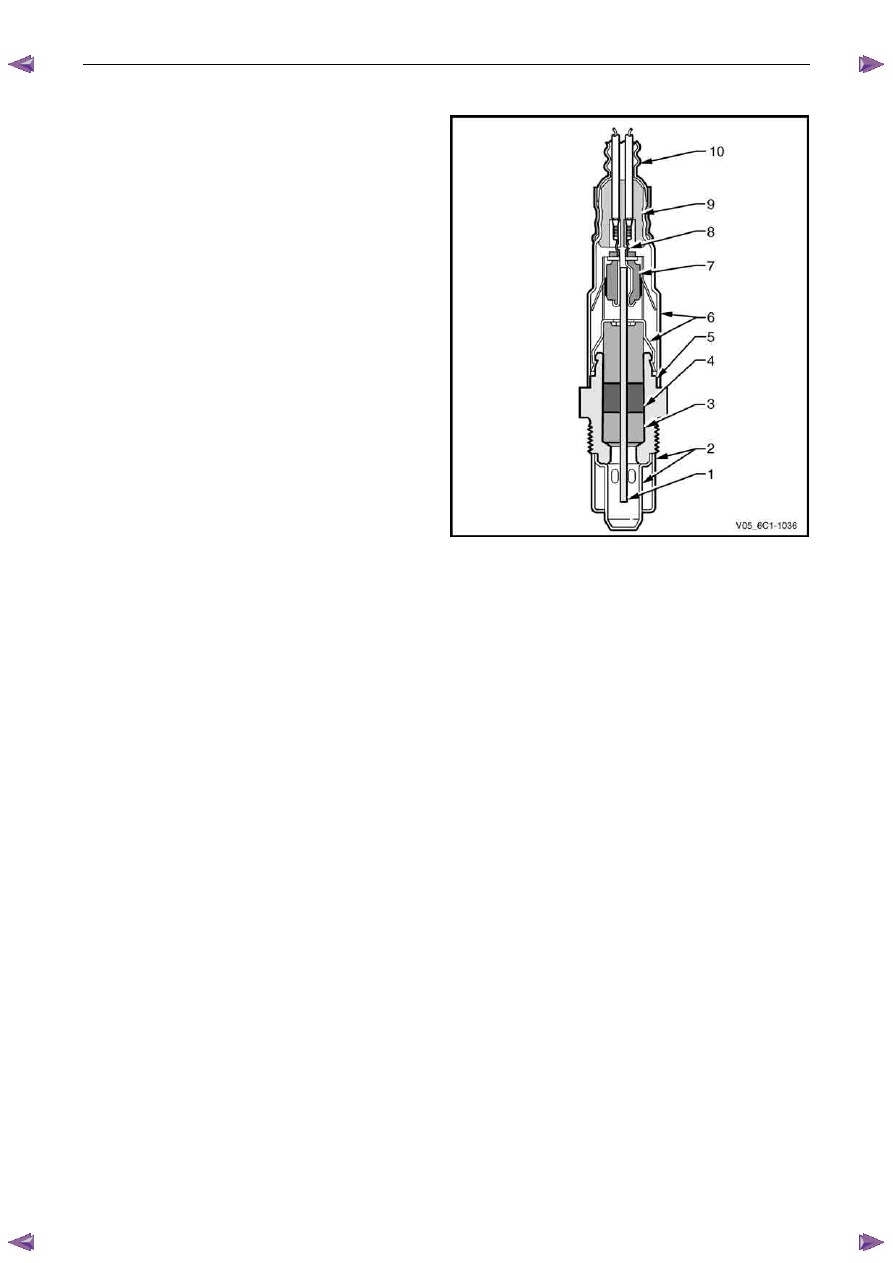
LSU 4.2 Wide-band Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors
The LSU 4.2 wide-band planar heated oxygen sensors have
six wires:
•
The internal heater element supply, which has 12 V
continually applied whenever the ignition is on.
•
Heater element ground – The ECM applies pulse
width modulated (PWM) ground to the HO2S heater
control circuit to control the rate at which the sensor
heats up. This reduces the risk of the sensor being
damaged from heating up too quickly under certain
conditions such as extreme cold temperatures. Once
the sensor has reached the desired operating
temperature, the ECM will monitor and continue to
maintain the sensor temperature.
•
Output voltage.
•
Sensor ground.
•
Trim current.
•
Pumping current.
Legend
1
Measuring Cell (Nernst cell and pump cell)
2
Double Protective Tube
3 Seal
Ring
4 Seal
Packing
5 Sensor
Housing
6 Protective
Sleeve
7 Contact
Holder
8 Contact
Clip
9
PTFE Sleeve (Teflon)
10
PTFE Shaped Sleeve
Figure 6C1-1 – 35

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст