Isuzu KB P190. Manual — part 845
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–102
3-way catalytic converter damage. The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will flash ON and OFF when the conditions for
catalytic converter damage are present. DTCs P0301 through P0306 correspond to cylinders 1 through 6. If the ECM is
able to determine that a specific cylinder is misfiring, the DTC for that cylinder will set. If the misfire rate is sufficient to
cause emission levels to exceed a predetermined value, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
•
DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, or P0338 are not set.
•
The engine speed is between 400 – 7,000 rpm and steady.
•
The delivered torque signal is more than 10 percent at idle.
•
The delivered torque signal is between 9 – 30 percent with the transmission in drive.
•
The intake air temperature (IAT) is more than –30° C.
•
The fuel level is more than 12 percent.
•
The torque management is not active.
•
DTC P0300 runs continuously when the above conditions exist for at least 1,000 engine revolutions.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
•
The ECM detects a crankshaft rotation speed variation indicating a misfire rate sufficient to cause emissions levels
to exceed mandated standards.
•
The condition above exists for more than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
•
The control module activates the MIL on the second ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
•
The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic
fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the
second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
•
The ECM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after four consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
•
A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
•
A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
•
Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
•
A misfire DTC could be caused by an excessive vibration from sources other than the engine. Inspect for the
following possible sources:
−
A tyre or wheel that is out of round or out of balance
−
Variable thickness brake rotors
−
An unbalanced drive shaft
−
Certain rough road conditions
−
A damaged accessory drive component or belt
•
A misfire DTC could be caused by a camshaft actuator stuck in the full advance or retard position.
•
For an intermittent condition, refer to 5.2
Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–103
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2
This step determines if there is a current condition.
4
If the Misfire Current Counters are incrementing, but the engine is NOT misfiring, this indicates a mechanical
condition. For example, an accessory drive belt could cause this condition.
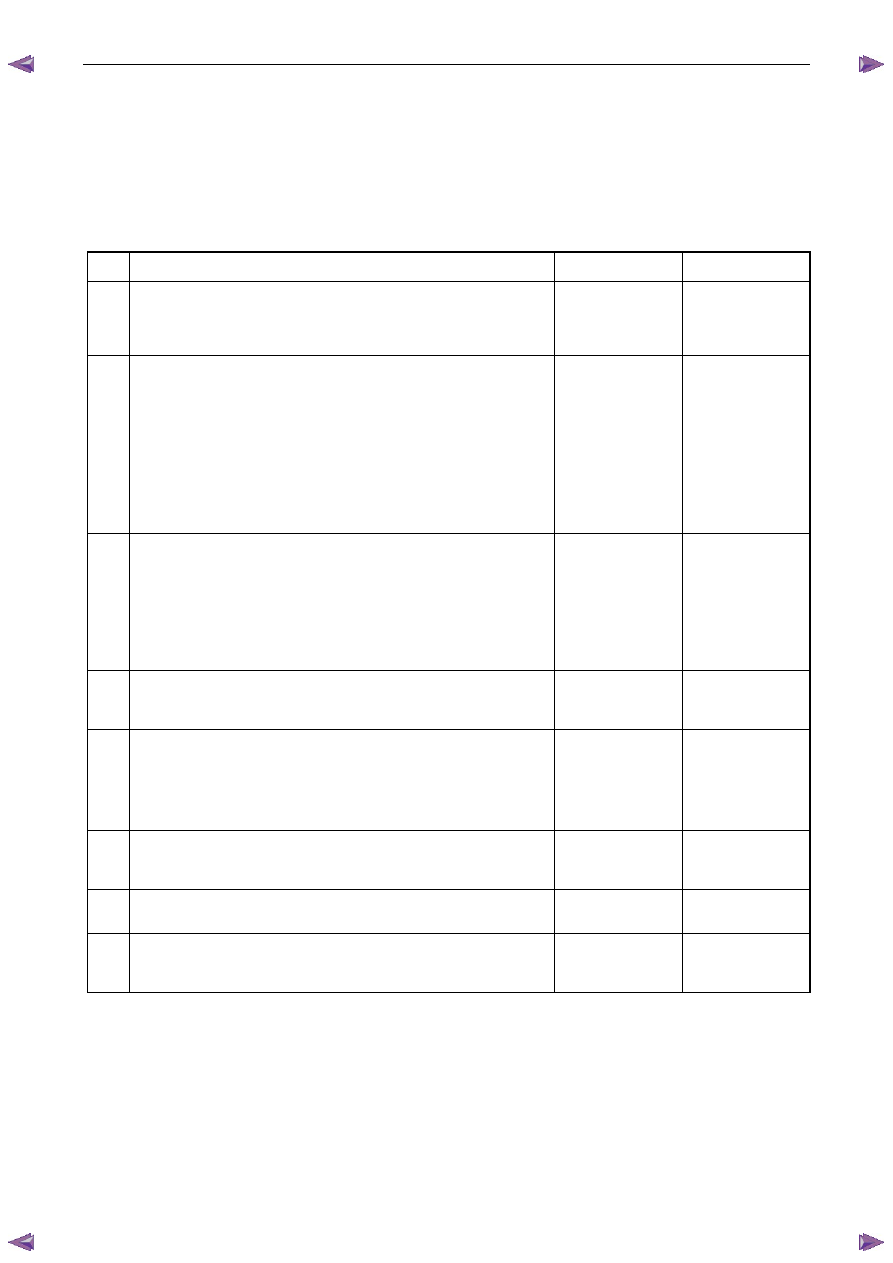
DTC P0300 - Engine Misfire Detected
Step Action
Yes
No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in
this Section
2
N O T E
The engine may only misfire when the engine is under a
load. An engine load may be necessary to verify the
condition.
1
Start the engine.
2
Use Tech 2 to monitor the Misfire Current Cyl 1 – 6 parameters.
Are any of the Misfire Current Counters incrementing?
Go to Step 4.
Go to Step 3
3
1
Clear the DTC.
1
Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2
Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3
Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0300 fail this ignition cycle?
Go to Step 4
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
4
Is the engine misfiring?
Go to Step 5
Go to Symptoms
Diagnostics in this
Section
5
1
Observe the DTC information using Tech 2.
Is DTC P0201-P0206, P0261, P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268,
P0270, P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276, P0277, P0335, P0336, P0338,
P0351-P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315, or P2316 also set?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section
Go to Step 6
6
Is there an engine mechanical noise?
Go to Symptoms in
6A1 Engine
Mechanical
Go to Step 7
7
Is there more than one cylinder specific misfire DTC set?
Go to Step 8
Go to
DTC 301 – 306
8
Are there any heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) DTCs set?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section
Go to Step 9
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–104
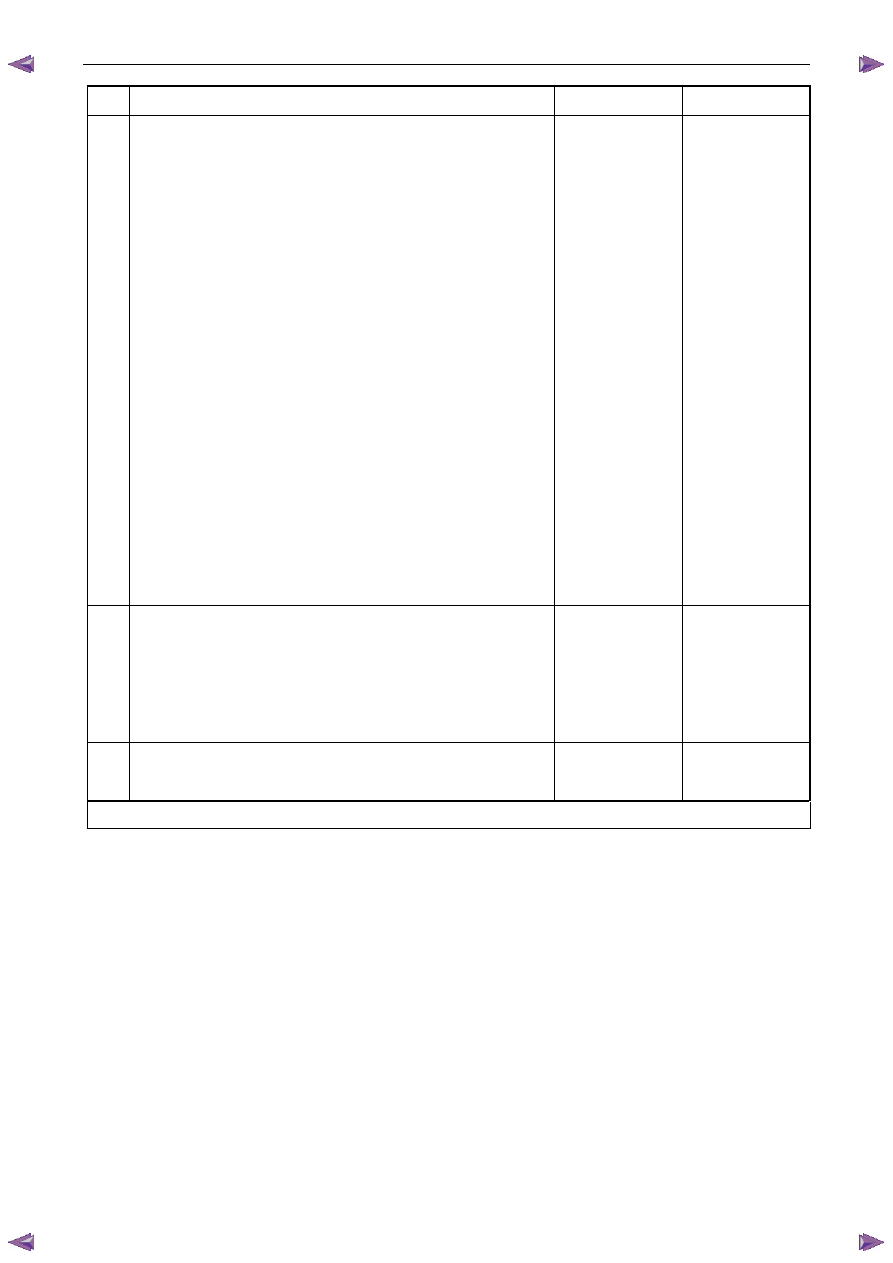
Step Action
Yes
No
9
1
Inspect or test for the following conditions:
•
Inspect the vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections.
•
Inspect the throttle body and the intake manifold for
vacuum leaks.
•
Inspect the crankcase ventilation valve and / or system for
any vacuum leaks.
•
Test for the correct fuel pressure. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
•
Inspect the fuel system for any restrictions, leaks or fuel
contamination. Refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
•
Inspect for fouled or damaged spark plugs. Determine
what caused the spark plugs to foul. Refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – Service Operations.
•
Inspect the exhaust system for restrictions. Refer to 6F
Exhaust System – V6.
•
Inspect the engine control grounds for being clean, tight,
and in the correct location.
•
Inspect for a camshaft actuator stuck in the full advance or
retard position.
2
Repair as required.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10
Go to Symptoms in
6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6
10
1
Use Tech 2 to clear the DTCs.
2
Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3
Start the engine.
4
Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running DTC 300.
Did the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 2
Go to Step 11
11
1
Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section
System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and verify correct operation
7.17 DTC P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305
or P0306
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
•
DTC P0301 – Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
•
DTC P0302 – Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
•
DTC P0303 – Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
•
DTC P0304 – Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected
•
DTC P0305 – Cylinder 5 Misfire Detected
•
DTC P0306 – Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–105
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses information from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor to determine when an engine misfire is occurring. By monitoring variations in the crankshaft rotation
speed for each cylinder, the ECM is able to detect individual misfire events. A misfire rate that is high enough can cause
3-way catalytic converter damage. The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will flash ON and OFF when the conditions for
catalytic converter damage are preset. DTCs P0301 – P0306 correspond to cylinders 1 to 6. If the ECM is able to
determine that a specific cylinder is misfiring, the DTC for that cylinder sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
•
DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, or P0338 are not set.
•
The engine speed is between 400 – 7,000 rpm and steady.
•
The delivered torque signal is more than 10 percent at idle with the transmission in neutral.
•
The delivered torque signal is between 10 – 30 percent with the transmission in drive.
•
The intake air temperature (IAT) is more than –30° C.
•
The engine run time is more than 45 seconds.
•
The fuel level is more than 12 percent.
•
The torque management is not active.
•
DTCs P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, and P0306 run continuously when the above conditions exist for at
least 1,000 engine revolutions.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
•
The ECM detects a crankshaft rotation speed variation indicating a single cylinder misfire rate sufficient to cause
emissions levels to exceed mandated standards.
•
The condition exists for more than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
•
The control module activates the MIL on the second ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
•
The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic
fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the
second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
•
The ECM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after four consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
•
A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
•
A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
•
Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
•
A misfire DTC could be caused by an excessive vibration from sources other than the engine. Check for the
following possible sources:
−
Tyre or wheel out of round or balance
−
Variable thickness brake rotor or drum
−
Drive shaft not balanced
−
Certain rough road conditions

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст