Isuzu KB P190. Manual — part 847
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–110
7.19 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 or P0333
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
•
DTC P0327 – Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 1)
•
DTC P0328 – Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 1)
•
DTC P0332 – Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 2)
•
DTC P0333 – Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The ECM supplies the ground to the knock sensor (KS) low reference circuit. The KS produces a signal voltage, which is
proportional to the level of the engine vibration or spark knock.
When the ECM detects an excessive spark knock, it retards the ignition timing until the spark knock stops.
To differentiate between a normal engine vibration and the vibration created by a spark knock, the ECM samples the KS
signal under different engine speeds and load condition. The ECM uses this samples to determine maximum and
minimum KS signal voltage produced when the engine is running under normal conditions.
A knock sensor circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the KS signal voltage is outside the normal range.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0327 and P0332
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
•
DTCs P0324, P0335, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed.
•
The ECM controls the ignition spark.
•
Engine speed is greater than 2000 rpm and steady.
•
The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60ºC.
•
The volumetric efficiency is steady.
DTC P0328 or P0333
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
•
The ECM controls the ignition spark.
•
Engine speed is greater than 2,000 rpm and steady.
•
The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60
°C.
•
The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0327 and P0332
The ECM detects the KS signal voltage is less than the minimum KS signal normal range for at least 10 seconds.
DTC P0328 and P0333
The ECM detects the KS signal voltage is greater than the maximum KS signal normal range.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The knock sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–111
Additional Information
•
Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the knock sensor (KS) system
operation.
•
Preconditions for running knock sensor circuit DTCs requires that DTC P0324 has ran and passed. Therefore, the
diagnostic table for the knock sensor circuit DTCs is developed with the assumption the ECM internal KS circuitry
is functioning correctly.
•
Excessive engine mechanical noise or engine knocking condition may trigger knock sensor circuit DTCs.
•
The knock sensor must be tightened correctly. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
•
The mounting between the knock sensor and engine must be free of burrs, casting flash and foreign material.
•
The knock sensor head must be clear from hoses, brackets and engine wiring.
•
If the knock sensor lead is damaged in any way, the sensor must be replaced.
•
Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
•
To assist diagnosis, refer to 3
Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3
Identifies engine mechanical fault conditions that may trigger knock sensor circuit DTCs.
4
Identifies KS fault conditions that may trigger knock sensor circuit DTCs.
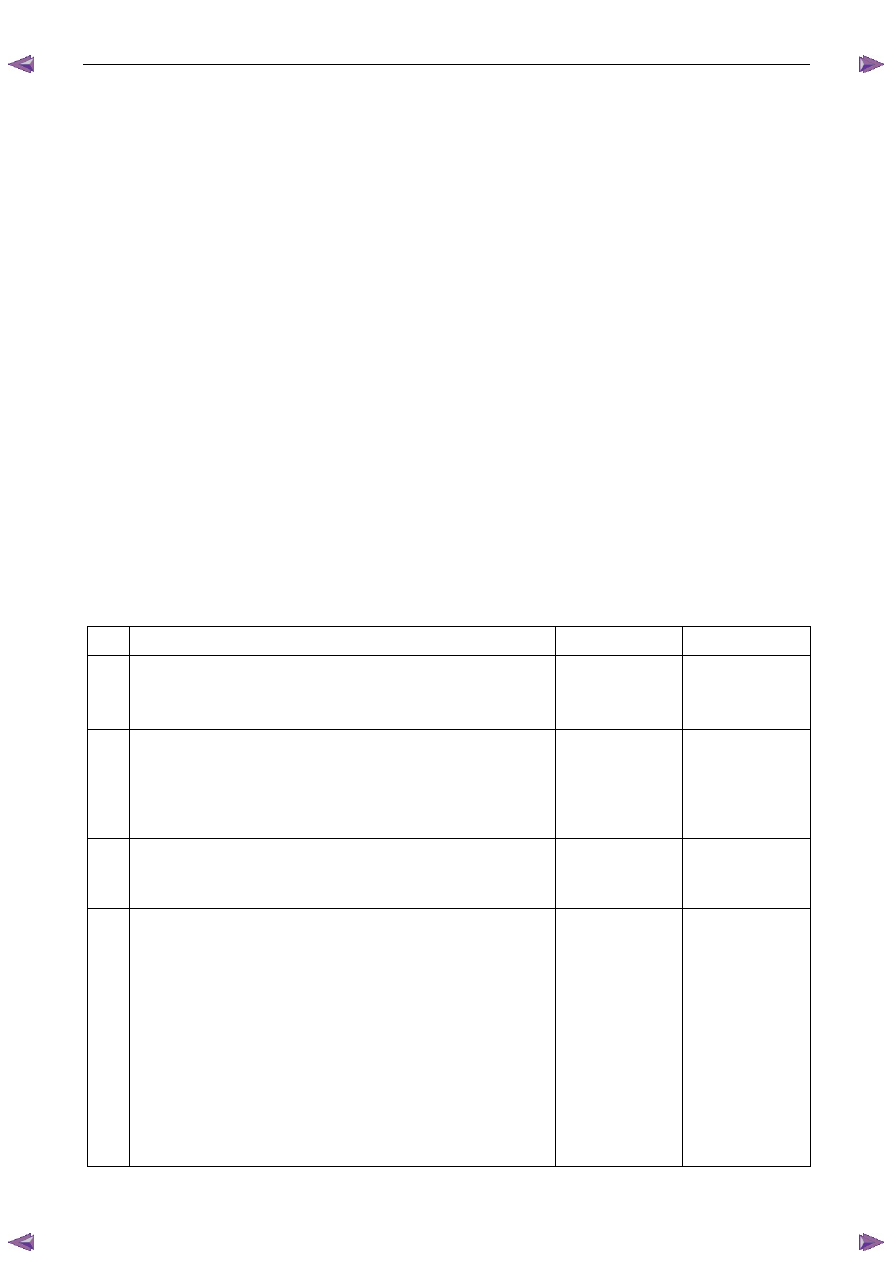
DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 Diagnostic Table
Step Action
Yes
No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in
this Section
2
1
Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2
Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3
Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 or P0333 fail this ignition cycle?
Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
DTC
3
Check the engine for excessive mechanical engine noise or engine
knocking fault condition. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified?
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 4
4
Inspect the appropriate KS for the following fault condition. Refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
•
incorrect KS attaching bolt torque value,
•
burrs, casting flash or foreign material between the knock
sensor and engine,
•
hoses, brackets or engine wiring touching the KS, and
•
damaged KS wiring harness.
•
sensor wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to 5.2
Intermittent Fault
Conditions in this Section.
Was any fault found and rectified?
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 5
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–112
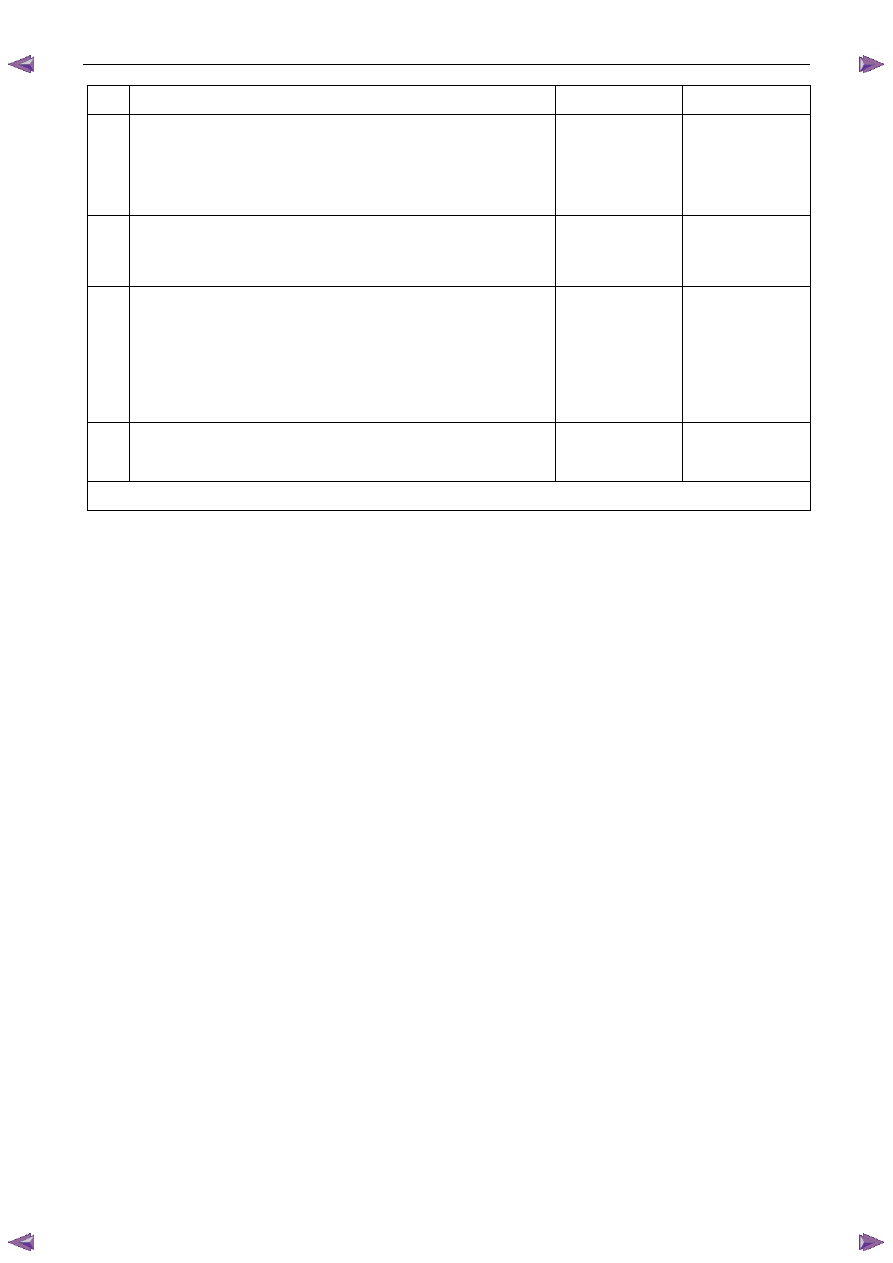
Step Action
Yes
No
5
Test the appropriate KS signal circuit and low reference circuit for a
high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage or
shorted together fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and
Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified?
Go to Step 7
Go to Step 6
6
Replace the faulty KS. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed?
Go to Step 7
—
7
1
Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2
Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3
Start the engine.
4
Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the knock sensor circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle?
Go to Step 2
Go to Step 8
8
Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section
System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.20 DTC P0335, P0336, P0337 or P0338
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
•
DTC P0335 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
•
DTC P0336 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Signal Range / Performance
•
DTC P0337 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Duty Cycle
•
DTC P0338 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit High Duty Cycle
Circuit Description
The ECM applies the ground to the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor low reference circuit.
The CKP sensor in conjunction with the 58X reluctor wheel generates an AC signal voltage. The amplitude and
frequency of the signal generated is proportional to the engine speed. The ECM uses this signal from the CKP sensor
signal circuit to determine the engine rpm
In addition, the CKP sensor sends a signal to the ECM when piston No. 1 and piston No. 4 are at the top dead centre
position. The ECM monitors both the CKP signal and the camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal to determine the
compression stroke of piston No. 1.
A CKP sensor DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the CKP sensor signal circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0335
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
•
The engine is cranking or running.
•
The ECM detects greater than 8 CMP sensor pulses.
DTC P0336
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–113
•
DTCs P0341, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed.
•
The engine is cranking or running.
•
The ECM detects a valid CMP signal.
DTC P0337 and P0338
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
•
DTCs P0341, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed.
•
The engine is cranking or running.
•
The ECM detects a valid CMP signal.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0335
The ECM does not detect a signal from the CKP sensor for 5 seconds.
DTC P0336
The ECM loses the crankshaft reference position and has to re-synchronise the crankshaft to camshaft one or more
times during six consecutive crankshaft revolutions.
DTC P0337
The ECM detects less than 58 reference signal pulses from the CKP sensor in the last eight consecutive crankshaft
revolutions.
DTC P0338
The ECM detects more than 58 reference signal pulses from the CKP sensor in the last eight consecutive crankshaft
revolutions.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The CKP sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
•
Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CKP sensor operation.
•
For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2
Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
•
If the ECM has stored and learned the camshafts reference position, the ECM will utilise the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor signal in place of the CKP signal when there is fault condition in the CKP circuit. This will enable the
engine to operate in a limp mode when there is a CKP circuit fault condition.
•
During a limp mode, the following DTCs may set and should be ignored.
•
DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor Module Performance
•
DTC P01011 – Intake Camshaft Position Actuator Park Position Bank 1
•
The following fault condition may trigger DTC P0338:
•
Fault condition in the CMP sensor circuits.
•
Misaligned CKP sensor reluctor wheel or incorrect reluctor wheel installation.
•
Excessive crankshaft end play that alters the alignment of the reluctor wheel.
•
Obstruction between the CKP sensor and the reluctor wheel.
•
Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст