Chrysler Le Baron, Dodge Dynasty, Plymouth Acclaim. Manual — part 31
once the system has entered closed loop. Refer to
Modes of Operation in this section for an explanation
of closed loop operation.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. Diagnostic trou-
ble codes may not be displayed for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause di-
agnostic trouble codes to be displayed for other sys-
tems. For example, a fuel pressure problem will not
register a fault directly, but could cause a rich or
lean condition. This could cause an oxygen sensor
fault to be stored in the PCM.
Fuel Pressure - Fuel pressure is controlled by the
fuel pressure regulator. The PCM cannot detect a
clogged fuel pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel fil-
ter, or a pinched fuel supply or return line. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing
an oxygen sensor fault.
Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn
spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug
cables.
Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. The PCM also cannot detect an
incorrectly indexed distributor. However, these could
result in a rich or lean condition causing an oxygen
sensor fault to be stored in the PCM.
Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression.
Exhaust System - The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system.
Fuel Injector Malfunctions - The PCM cannot
determine if the fuel injector is clogged, the pintle is
sticking or the wrong injector is installed. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing
an oxygen sensor fault to be stored in the PCM.
Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors the exhaust stream oxygen content through
the oxygen sensor when the system is in closed loop,
it cannot determine excessive oil consumption.
Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect
a clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter ele-
ment.
Evaporative System - The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded evaporative purge can-
ister.
Vacuum Assist - Leaks or restrictions in the vac-
uum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control sys-
tem devices are not monitored by the PCM. However,
these could result in a MAP sensor fault being stored
in the PCM.
PCM System Ground - The PCM cannot deter-
mine a poor system ground. However, a diagnostic
trouble code may be generated as a result of this con-
dition.
PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a diagnostic trouble code may be generated as a
result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device with es-
tablished high and low limits that are programmed
into it for that device. If the input voltage is not
within specifications and other diagnostic trouble
code criteria are met, a diagnostic trouble code will
be stored in memory. Other diagnostic trouble code
criteria might include engine RPM limits or input
voltages from other sensors or switches that must be
present before a fault condition can be verified.
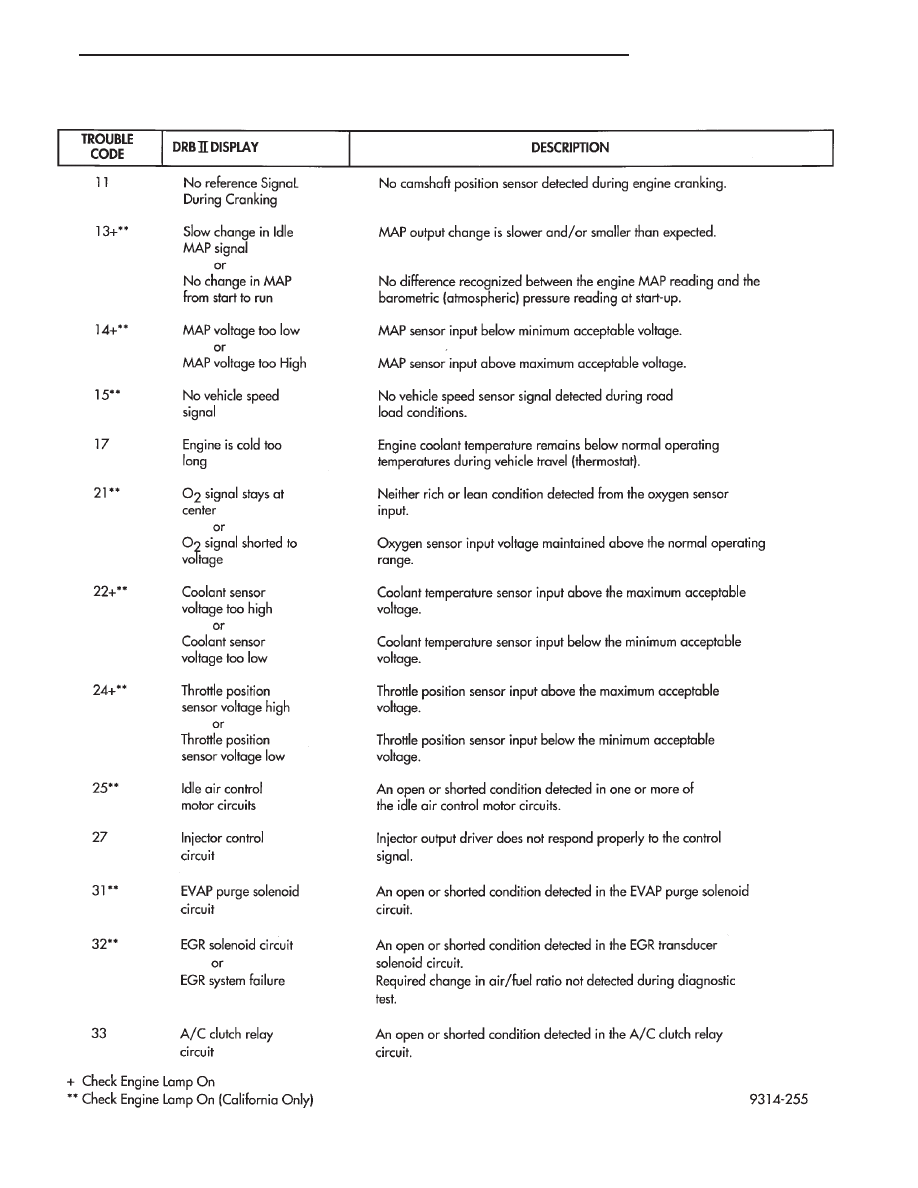
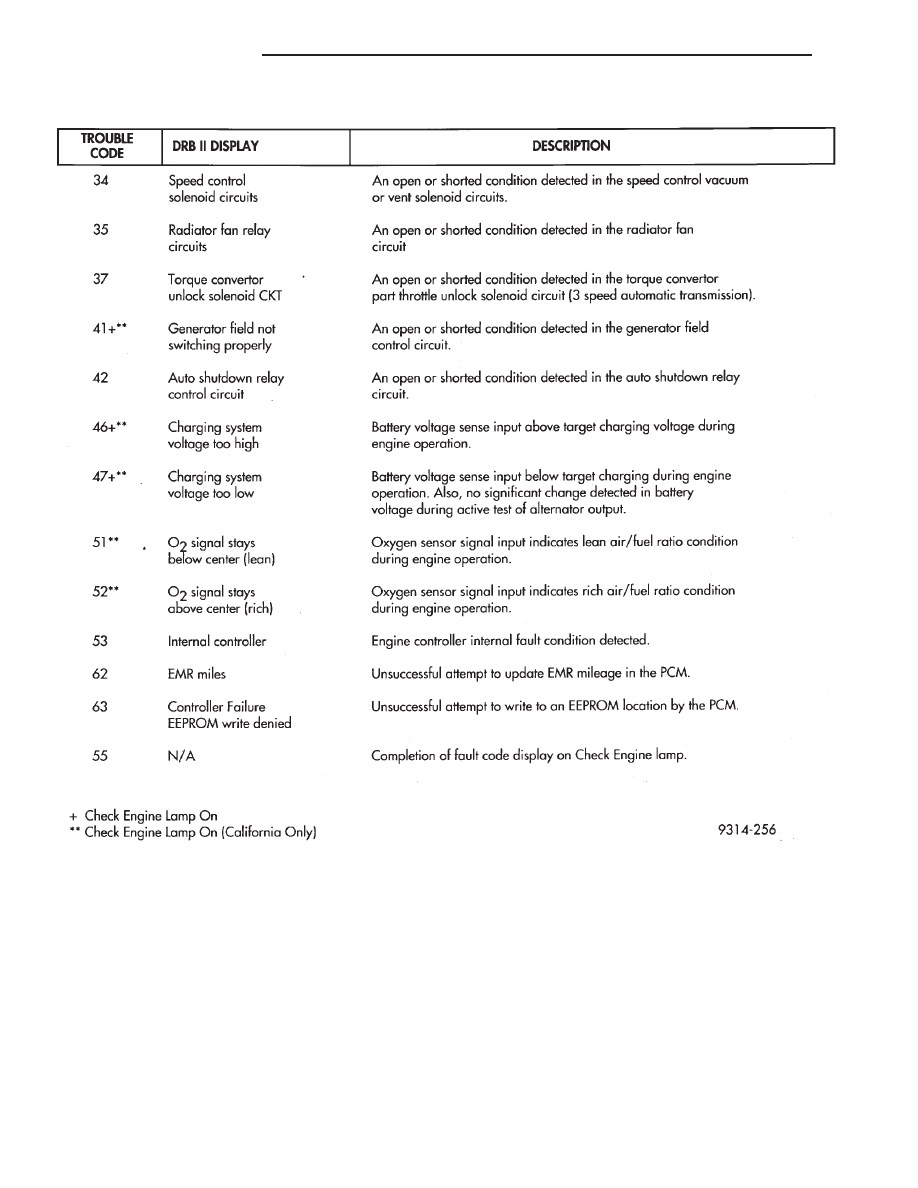
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
When a diagnostic trouble code appears, it indi-
cates the powertrain control module (PCM) has rec-
ognized
an
abnormal
condition
in
the
system.
Diagnostic trouble codes can be obtained from the
malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel Check
Engine lamp) on the Instrument Panel or from the
DRBII scan tool. Diagnostic trouble codes indicate
the results of a failure but do not identify the failed
component directly.
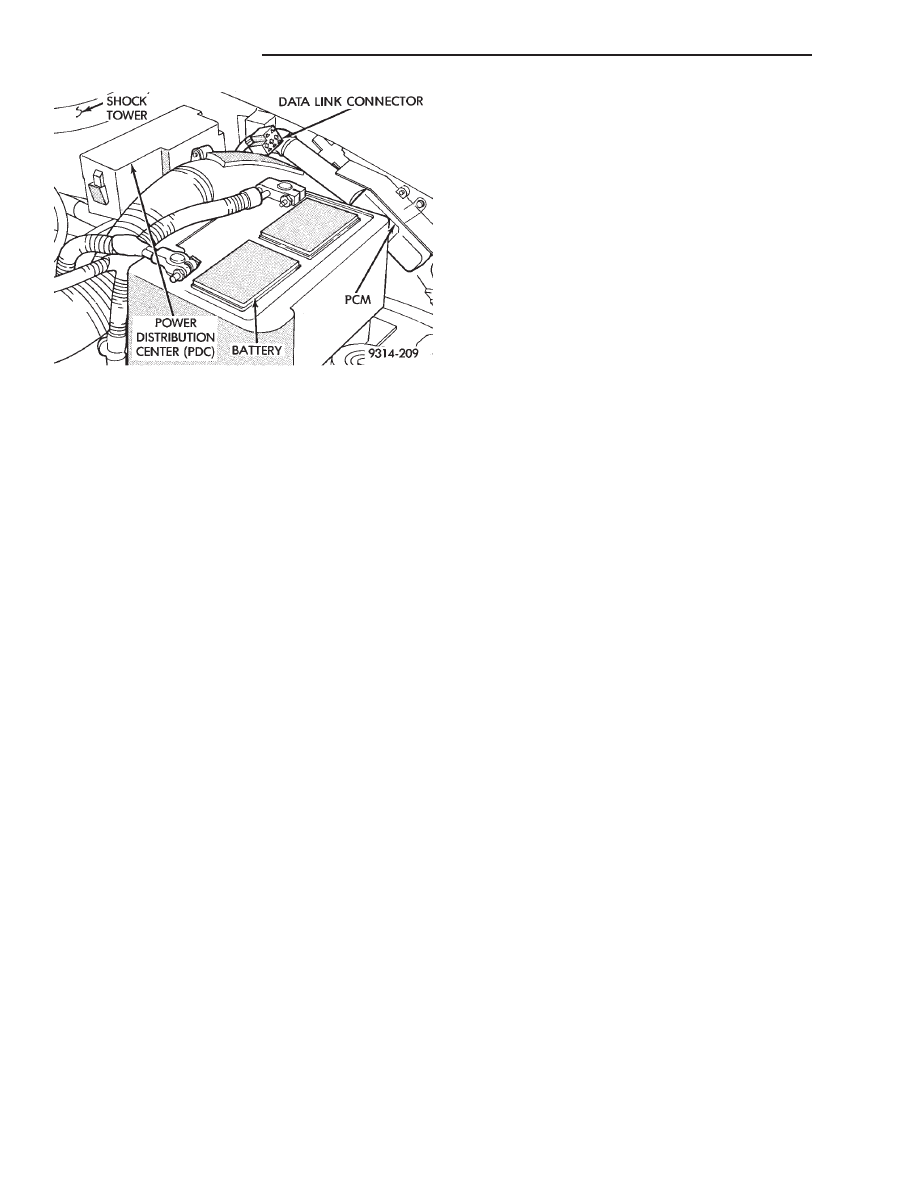
Fig. 3 Data Link Connector Location—AG and AJ
Vehicles
14 - 42
FUEL SYSTEMS
Ä
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
Ä
FUEL SYSTEMS
14 - 43
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
14 - 44
FUEL SYSTEMS
Ä
SYSTEMS TEST
WARNING:
APPLY
PARKING
BRAKE
AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING A TEST
WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link con-
nector located in the engine compartment near the
powertrain control module (PCM).
(2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/C switch if applicable. Shut off
the engine.
(3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel).
The lamp should light for 3 seconds then go out (bulb
check).
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states,
HIGH and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot
recognize the difference between a selected switch po-
sition versus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a de-
fective switch. If the change is displayed, it can be
assumed that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is
functional. From the state display screen access ei-
ther State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Dis-
play Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen.
Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle only)
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C (Speed Control) Vent Solenoid
S/C (Speed Control) Vacuum Solenoid
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid (3 speed auto-
matic transaxle)
A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen.
Oxygen Sensor Signal
Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Added Adaptive Fuel
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idl Spd
Engine Speed
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-On Info
Fault #3 Key-On Info
Speed Control Status
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Speed Control Switch Voltage
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The circuit actuation test mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices which the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) cannot internally rec-
ognize. The PCM can attempt to activate these
outputs and allow an observer to verify proper oper-
ation. Most of the tests provide an audible or visual
indication of device operation (click of relay contacts,
spray fuel, etc.). With the exception of an intermit-
tent condition, if a device functions properly during
its test, it can be assumed that the device, its associ-
ated wiring, and its driver circuit are in working or-
der.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the
engine
control
system
functions
accessible
through Actuators screens.
Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Fuel Injector #1
Idle Air Control Motor Open/Close
Ä
FUEL SYSTEMS
14 - 45

Нет комментариевНе стесняйтесь поделиться с нами вашим ценным мнением.
Текст